Hannibal
Hannibal Barca | |
|---|---|
 A marble bust, reputedly of Hannibal, originally found at the ancient city-state of Capua in Italy | |
| Native name | .mw-parser-output .script-phoenician{font-family:"ALPHABETUM Unicode","MPH 2B Damase",Aegean,Code2001,"Noto Sans Phoenician",FreeSans,"Segoe UI Historic",sans-serif} 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋 𐤁𐤓𐤒 |
| Born | 247 BC Carthage |
| Died | 183/181 BC Libyssa |
| Allegiance |
|
| Rank | General Commander-in-Chief of the Carthaginian army |
| Wars | .mw-parser-output .treeview ul{padding:0;margin:0}.mw-parser-output .treeview li{padding:0;margin:0;list-style-type:none;list-style-image:none}.mw-parser-output .treeview li li{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f2/Treeview-grey-line.png")no-repeat 0 -2981px;padding-left:21px;text-indent:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .treeview li li:last-child{background-position:0 -5971px}.mw-parser-output .treeview li.emptyline>ul>.mw-empty-elt:first-child+.emptyline,.mw-parser-output .treeview li.emptyline>ul>li:first-child{background-position:0 9px}
|
| Spouse(s) | Imilce |
| Relations | Hasdrubal Barca Mago Barca Hasdrubal the Fair |
Hannibal Barca (/ˈhænɪbəl/; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC)[n 1] was a general of the Phoenician state of Ancient Carthage, and is widely considered as one of the greatest military commanders in history. His father Hamilcar Barca was the leading Carthaginian commander during the First Punic War. His younger brothers were Mago and Hasdrubal, and he was brother-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair.
Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the western Mediterranean Basin, when the Roman Republic established its supremacy over other great powers such as ancient Carthage, the Etruscans, the Samnites, and the Greek kingdom of Syracuse. One of his most famous achievements was at the outbreak of the Second Punic War, when he marched an army which included war elephants from Iberia over the Pyrenees and the Alps into Italy. In his first few years in Italy, he won dramatic victories at the Trebia, Lake Trasimene, and Cannae. He distinguished himself for his ability to determine his and his opponent's respective strengths and weaknesses, and to plan battles accordingly. Hannibal's well-planned strategies allowed him to conquer many allies of Rome.
Hannibal occupied part of Italy, specifically southern Italy, for 15 years but was unable to march on Rome. An enemy counter-invasion of North Africa forced him to return to Carthage, where he was decisively defeated by Scipio Africanus at the Battle of Zama. Scipio had studied Hannibal's tactics and brilliantly devised some of his own, and he finally defeated Rome's nemesis at Zama, having previously driven Hannibal's brother Hasdrubal out of the Iberian Peninsula.
After the war, Hannibal successfully ran for the office of sufet. He enacted political and financial reforms to enable the payment of the war indemnity imposed by Rome; however, those reforms were unpopular with members of the Carthaginian aristocracy and in Rome, and he fled into voluntary exile. During this time, he lived at the Seleucid court, where he acted as military advisor to Antiochus III the Great in his war against Rome. Antiochus met defeat at the Battle of Magnesia and was forced to accept Rome's terms, and Hannibal fled again, making a stop in the Kingdom of Armenia. His flight ended in the court of Bithynia, where he achieved an outstanding naval victory against a fleet from Pergamon. He was afterwards betrayed to the Romans and committed suicide by poisoning himself.
Hannibal is often regarded as one of the greatest military strategists in history and one of the greatest generals of Mediterranean antiquity, together with Philip of Macedon, Alexander the Great, Julius Caesar, and Scipio Africanus. Plutarch states that Scipio asked Hannibal who was the greatest general, and Hannibal replied either Alexander or Pyrrhus, then himself[1] (or Pyrrhus, Scipio, then himself, according to another version of the event).[2] Military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge called Hannibal the "father of strategy",[3] because his enemy Rome adopted elements of his military tactics in its own strategic arsenal. This praise has earned him a strong reputation in the modern world, and he was regarded as a great strategist by Napoleon and others.
Contents
1 Name
2 Background and early career
3 Second Punic War in Italy (218–204 BC)
3.1 Overland journey to Italy
3.2 Battle of Trebia
3.3 Battle of Lake Trasimene
3.4 Battle of Cannae
3.5 Stalemate
3.6 Hannibal's retreat in Italy
4 Conclusion of the Second Punic War (203–201 BC)
4.1 Return to Carthage
4.2 Battle of Zama (202 BC)
5 Later career
5.1 Peacetime Carthage (200–196 BC)
5.2 Exile (after 195 BC)
5.3 Death (183 to 181 BC)
6 Legacy
6.1 Legacy to the ancient world
6.2 Military history
7 Timeline
8 See also
9 Notes
10 References
10.1 Citations
10.2 Bibliography
11 Further reading
12 External links
Name
The English form of the name is derived from the Latin. Greek historians rendered the name as Anníbas Bárkas (Ἀννίβας Βάρκας).
Hannibal was a common Phoenician-Carthaginian masculine given name. The name was recorded in Carthaginian sources as ḤNBʿL[4] (Punic: 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋). It is a combination of the common Carthaginian masculine given name Hanno with the Northwest Semitic Phoenician-Canaanite deity Baal (lit. "The Lord"). Its precise vocalization remains a matter of debate. Suggested readings include Ḥannobaʿal,[5]Ḥannibaʿl, or Ḥannibaʿal,[6][7] meaning "Baʿal/The Lord is Gracious", "Baʿal Has Been Gracious",[7][8] or "The Grace of Baʿal".[6]
Barca (Punic: 𐤁𐤓𐤒, BRQ) was the Semitic surname of his aristocratic family, meaning "shining" or "lightning".[9] It is thus the Phoenician equivalent to the Arabic name Barq or the Hebrew name Barak or the ancient Greek epithet Keraunos, which was commonly given to military commanders in the Hellenistic period.[10]
In English, his clan are sometimes collectively known as the Barcids. As with Greek and Roman practice, patronymics were a common part of Carthaginian nomenclature, so that Hannibal would also have been known as "Hannibal son of Hamilcar".[11]
Background and early career

A Carthaginian coin depicting Hasdrubal Barca (245–207 BC), one of Hannibal's younger brothers, wearing a diadem

A Carthaginian shekel, dated 237–227 BC, depicting the Punic god Melqart (equivalent of Hercules/Heracles), most likely with the features of Hamilcar Barca, father of Hannibal Barca; on the reverse is a man riding an elephant

A quarter shekel of Carthage, perhaps minted in Spain; the obverse may depict Hannibal with the traits of a young Melqart; the reverse features one of his famous war elephants.[12]
Hannibal was one of the sons of Hamilcar Barca, a Carthaginian leader. He was born in what is present day northern Tunisia, one of many Mediterranean regions colonised by the Phoenicians from their homelands in the Near East. He had several sisters and two brothers, Hasdrubal and Mago. His brothers-in-law were Hasdrubal the Fair and the Numidian king Naravas. He was still a child when his sisters married, and his brothers-in-law were close associates during his father's struggles in the Mercenary War and the Punic conquest of the Iberian Peninsula. In light of Hamilcar Barca's cognomen, historians refer to Hamilcar's family as the Barcids. However, there is debate as to whether the cognomen Barca (meaning "thunderbolt") was applied to Hamilcar alone or was hereditary within his family. If the latter, then Hannibal and his brothers also bore the name "Barca".[13]
After Carthage's defeat in the First Punic War, Hamilcar set out to improve his family's and Carthage's fortunes. With that in mind and supported by Gades, Hamilcar began the subjugation of the tribes of the Iberian Peninsula. Carthage at the time was in such a poor state that it lacked a navy able to transport his army; instead, Hamilcar had to march his forces across Numidia towards the Pillars of Hercules and then cross the Strait of Gibraltar.[14]
According to Polybius, Hannibal much later said that when he came upon his father and begged to go with him, Hamilcar agreed and demanded that he swear that as long as he lived he would never be a friend of Rome. There is even an account of him at a very young age (9 years old) begging his father to take him to an overseas war. In the story, Hannibal's father took him up and brought him to a sacrificial chamber. Hamilcar held Hannibal over the fire roaring in the chamber and made him swear that he would never be a friend of Rome. Other sources report that Hannibal told his father, "I swear so soon as age will permit...I will use fire and steel to arrest the destiny of Rome."[3][15] According to the tradition, Hannibal's oath took place in the town of Peñíscola, today part of the Valencian Community, Spain.[16]
Hannibal's father went about the conquest of Hispania. When his father drowned[17] in battle, Hannibal's brother-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair succeeded to his command of the army with Hannibal (then 18 years old) serving as an officer under him. Hasdrubal pursued a policy of consolidation of Carthage's Iberian interests, even signing a treaty with Rome whereby Carthage would not expand north of the Ebro so long as Rome did not expand south of it.[18] Hasdrubal also endeavoured to consolidate Carthaginian power through diplomatic relationships with native tribes.[19]
Upon the assassination of Hasdrubal in 221 BC, Hannibal (now 26 years old) was proclaimed commander-in-chief by the army and confirmed in his appointment by the Carthaginian government. The Roman scholar Livy gives a depiction of the young Carthaginian: "No sooner had he arrived...the old soldiers fancied they saw Hamilcar in his youth given back to them; the same bright look; the same fire in his eye, the same trick of countenance and features. Never was one and the same spirit more skillful to meet opposition, to obey, or to command[.]"[20]
Livy also records that Hannibal married a woman of Castulo, a powerful Spanish city closely allied with Carthage.[21] The Roman epic poet Silius Italicus names her as Imilce.[22] Silius suggests a Greek origin for Imilce, but Gilbert Charles-Picard argued for a Punic heritage based on an etymology from the Semitic root m-l-k ('chief, the 'king').[23] Silius also suggests the existence of a son,[24] whom is otherwise not attested by Livy, Polybius, or Appian.
After he assumed command, Hannibal spent two years consolidating his holdings and completing the conquest of Hispania, south of the Ebro.[25] In his first campaign, Hannibal attacked and stormed the Olcades' strongest centre, Alithia, which promptly led to their surrender, and brought Punic power close to the River Tagus. His following campaign in 220 BC was against the Vaccaei to the west, where he stormed the Vaccaen strongholds of Helmantice and Arbucala. On his return home, laden with many spoils, a coalition of Spanish tribes, led by the Carpetani, attacked, and Hannibal won his first major battlefield success and showed off his tactical skills at the battle of the River Tagus.[26] However, Rome, fearing the growing strength of Hannibal in Iberia, made an alliance with the city of Saguntum, which lay a considerable distance south of the River Ebro and claimed the city as its protectorate. Hannibal not only perceived this as a breach of the treaty signed with Hasdrubal, but as he was already planning an attack on Rome, this was his way to start the war. So he laid siege to the city, which fell after eight months.[27]
Hannibal sent the booty from Saguntum to Carthage, a shrewd move which gained him much support from the government; Livy records that only Hanno II the Great spoke against him.[28] In Rome, the Senate reacted to this apparent violation of the treaty by dispatching a delegation to Carthage to demand whether Hannibal had destroyed Saguntum in accordance with orders from Carthage. The Carthaginian Senate responded with legal arguments observing the lack of ratification by either government for the treaty alleged to have been violated.[29] The delegation's leader, Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, demanded Carthage chose between war and peace, to which his audience replied that Rome could choose. Fabius chose war.[30]
Second Punic War in Italy (218–204 BC)
Overland journey to Italy
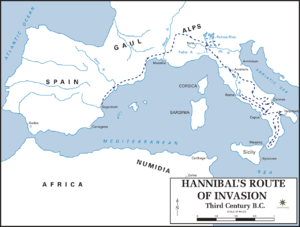
Hannibal´s route of invasion given by the Department of History, United States Military Academy. There is a mistake in the scale.
This journey was originally planned by Hannibal's brother-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair, who became a Carthaginian general in the Iberian Peninsula in 229 BC. He maintained this post for eight years until 221 BC. Soon the Romans became aware of an alliance between Carthage and the Celts of the Po Valley in Northern Italy. The Celts were amassing forces to invade farther south in Italy, presumably with Carthaginian backing. Therefore, the Romans preemptively invaded the Po region in 225 BC. By 220 BC, the Romans had annexed the area as Cisalpine Gaul.[31] Hasdrubal was assassinated around the same time (221 BC), bringing Hannibal to the fore. It seems that the Romans lulled themselves into a false sense of security, having dealt with the threat of a Gallo-Carthaginian invasion, and perhaps knowing that the original Carthaginian commander had been killed.
Hannibal departed New Carthage in late spring of 218 BC.[32] He fought his way through the northern tribes to the foothills of the Pyrenees, subduing the tribes through clever mountain tactics and stubborn fighting. He left a detachment of 20,000 troops to garrison the newly conquered region. At the Pyrenees, he released 11,000 Iberian troops who showed reluctance to leave their homeland. Hannibal reportedly entered Gaul with 40,000-foot soldiers and 12,000 horsemen.[33]
Hannibal recognized that he still needed to cross the Pyrenees, the Alps, and many significant rivers.[34] Additionally, he would have to contend with opposition from the Gauls, whose territory he passed through. Starting in the spring of 218 BC, he crossed the Pyrenees and reached the Rhône by conciliating the Gaulish chiefs along his passage before the Romans could take any measures to bar his advance, arriving at the Rhône in September. Hannibal's army numbered 38,000 infantry, 8,000 cavalry, and 38 elephants, almost none of which would survive the harsh conditions of the Alps.[35]

Hannibal and his men crossing the Alps.
Hannibal outmaneuvered the natives who had tried to prevent his crossing, then evaded a Roman force marching from the Mediterranean coast by turning inland up the valley of the Rhône. His exact route over the Alps has been the source of scholarly dispute ever since (Polybius, the surviving ancient account closest in time to Hannibal's campaign, reports that the route was already debated). The most influential modern theories favor either a march up the valley of the Drôme and a crossing of the main range to the south of the modern highway over the Col de Montgenèvre or a march farther north up the valleys of the Isère and Arc crossing the main range near the present Col de Mont Cenis or the Little St Bernard Pass.[36] Recent numismatic evidence suggests that Hannibal's army may have passed within sight of the Matterhorn.[37] Stanford geoarchaeologist Patrick Hunt argues that Hannibal took the Col de Clapier mountain pass, claiming the Clapier most accurately met ancient depictions of the route: wide view of Italy, pockets of year-round snow, and a large campground.[38] Other scholars have doubts, proposing that Hannibal took the easier route across Petit Mount Cenis. Hunt responds to this by proposing that Hannibal's Celtic guides purposefully misguided the Carthaginian general.
By Livy's account, the crossing was accomplished in the face of huge difficulties.[39] These Hannibal surmounted with ingenuity, such as when he used vinegar and fire to break through a rockfall.[40] According to Polybius, he arrived in Italy accompanied by 20,000-foot soldiers, 4,000 horsemen, and only a few elephants. The fired rockfall event is mentioned only by Livy; Polybius is mute on the subject and there is no evidence[41] of carbonized rock at the only two-tier rockfall in the Western Alps, located below the Col de la Traversette (Mahaney, 2008). If Polybius is correct in his figure for the number of troops that he commanded after the crossing of the Rhône, this would suggest that he had lost almost half of his force. Historians such as Serge Lancell have questioned the reliability of the figures for the number of troops that he had when he left Hispania.[42] From the start, he seems to have calculated that he would have to operate without aid from Hispania.
Hannibal's vision of military affairs was derived partly from the teaching of his Greek tutors and partly from experience gained alongside his father, and it stretched over most of the Hellenistic World of his time. Indeed, the breadth of his vision gave rise to his grand strategy of conquering Rome by opening a northern front and subduing allied city-states on the peninsula, rather than by attacking Rome directly. Historical events which led to the defeat of Carthage during the First Punic War when his father commanded the Carthaginian Army also led Hannibal to plan the invasion of Italy by land across the Alps.
The task was daunting, to say the least. It involved the mobilization of between 60,000 and 100,000 troops and the training of a war-elephant corps, all of which had to be provisioned along the way. The alpine invasion of Italy was a military operation that would shake the Mediterranean World of 218 BC with repercussions for more than two decades.
Battle of Trebia

A diagram depicting the tactics used in the Battle of the Trebia
Hannibal's perilous march brought him into the Roman territory and frustrated the attempts of the enemy to fight out the main issue on foreign ground. His sudden appearance among the Gauls of the Po Valley, moreover, enabled him to detach those tribes from their new allegiance to the Romans before the Romans could take steps to check the rebellion. Publius Cornelius Scipio was the consul who commanded the Roman force sent to intercept Hannibal (he was also Scipio Africanus' father). He had not expected Hannibal to make an attempt to cross the Alps, since the Romans were prepared to fight the war in the Iberian Peninsula. With a small detachment still positioned in Gaul, Scipio made an attempt to intercept Hannibal. He succeeded, through prompt decision and speedy movement, in transporting his army to Italy by sea in time to meet Hannibal. Hannibal's forces moved through the Po Valley and were engaged in the Battle of Ticinus. Here, Hannibal forced the Romans to evacuate the plain of Lombardy, by virtue of his superior cavalry.[43] The victory was minor, but it encouraged the Gauls and Ligurians to join the Carthaginian cause, whose troops bolstered his army back to around 40,000 men. Scipio was severely injured, his life only saved by the bravery of his son who rode back onto the field to rescue his fallen father. Scipio retreated across the Trebia to camp at Placentia with his army mostly intact.[43]
The other Roman consular army was rushed to the Po Valley. Even before news of the defeat at Ticinus had reached Rome, the Senate had ordered Consul Tiberius Sempronius Longus to bring his army back from Sicily to meet Scipio and face Hannibal. Hannibal, by skillful maneuvers, was in position to head him off, for he lay on the direct road between Placentia and Arminum, by which Sempronius would have to march to reinforce Scipio. He then captured Clastidium, from which he drew large amounts of supplies for his men. But this gain was not without loss, as Sempronius avoided Hannibal's watchfulness, slipped around his flank, and joined his colleague in his camp near the Trebia River near Placentia. There Hannibal had an opportunity to show his masterful military skill at the Trebia in December of the same year, after wearing down the superior Roman infantry, when he cut it to pieces with a surprise attack and ambush from the flanks.
Battle of Lake Trasimene
Hannibal quartered his troops for the winter with the Gauls, whose support for him had abated. In the spring of 217 BC, Hannibal decided to find a more reliable base of operations farther south. Gnaeus Servilius and Gaius Flaminius (the new consuls of Rome) were expecting Hannibal to advance on Rome, and they took their armies to block the eastern and western routes that Hannibal could use.[44]

Battle of Lake Trasimene, 217 BC.
From the Department of History, United States Military Academy
The only alternative route to central Italy lay at the mouth of the Arno. This area was practically one huge marsh, and happened to be overflowing more than usual during this particular season. Hannibal knew that this route was full of difficulties, but it remained the surest and certainly the quickest way to central Italy. Polybius claims that Hannibal's men marched for four days and three nights, "through a land that was under water", suffering terribly from fatigue and enforced want of sleep. He crossed without opposition over both the Apennines (during which he lost his right eye[45] because of conjunctivitis) and the seemingly impassable Arno, but he lost a large part of his force in the marshy lowlands of the Arno.[46]
He arrived in Etruria in the spring of 217 BC and decided to lure the main Roman army under Flaminius into a pitched battle by devastating the region that Flaminius had been sent to protect. As Polybius recounts, "he [Hannibal] calculated that, if he passed the camp and made a descent into the district beyond, Flaminius (partly for fear of popular reproach and partly of personal irritation) would be unable to endure watching passively the devastation of the country but would spontaneously follow him... and give him opportunities for attack."[47] At the same time, Hannibal tried to break the allegiance of Rome's allies by proving that Flaminius was powerless to protect them. Despite this, Flaminius remained passively encamped at Arretium. Hannibal marched boldly around Flaminius' left flank, unable to draw him into battle by mere devastation, and effectively cut him off from Rome (thus executing the first recorded turning movement in military history). He then advanced through the uplands of Etruria, provoking Flaminius into a hasty pursuit and catching him in a defile on the shore of Lake Trasimenus. There Hannibal destroyed Flaminius' army in the waters or on the adjoining slopes, killing Flaminius as well (see Battle of Lake Trasimene). This was the most costly ambush that the Romans ever sustained until the Battle of Carrhae against the Parthian Empire.
Hannibal had now disposed of the only field force that could check his advance upon Rome, but he realized that, without siege engines, he could not hope to take the capital. He preferred to exploit his victory by entering into central and southern Italy and encouraging a general revolt against the sovereign power.[48]
The Romans appointed Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus as their dictator. Departing from Roman military traditions, Fabius adopted the strategy named after him, avoiding open battle while placing several Roman armies in Hannibal's vicinity in order to watch and limit his movements.
Hannibal ravaged Apulia but was unable to bring Fabius to battle, so he decided to march through Samnium to Campania, one of the richest and most fertile provinces of Italy, hoping that the devastation would draw Fabius into battle. Fabius closely followed Hannibal's path of destruction, yet still refused to let himself be drawn out of the defensive. This strategy was unpopular with many Romans, who believed that it was a form of cowardice.
Hannibal decided that it would be unwise to winter in the already devastated lowlands of Campania, but Fabius had ensured that all the passes were blocked out of Campania. To avoid this, Hannibal deceived the Romans into thinking that the Carthaginian army was going to escape through the woods. As the Romans moved off towards the woods, Hannibal's army occupied the pass, and then made their way through the pass unopposed. Fabius was within striking distance but in this case his caution worked against him. Smelling a stratagem (rightly), he stayed put. For the winter, Hannibal found comfortable quarters in the Apulian plain. What Hannibal achieved in extricating his army was, as Adrian Goldsworthy puts it, "a classic of ancient generalship, finding its way into nearly every historical narrative of the war and being used by later military manuals".[49] This was a severe blow to Fabius' prestige and soon after this his period of dictatorial power ended.
Battle of Cannae

Destruction of the Roman army (red), courtesy of The Department of History, United States Military Academy
In the spring of 216 BC, Hannibal took the initiative and seized the large supply depot at Cannae in the Apulian plain. By capturing Cannae, Hannibal had placed himself between the Romans and their crucial sources of supply.[50] Once the Roman Senate resumed their consular elections in 216 BC, they appointed Gaius Terentius Varro and Lucius Aemilius Paullus as consuls. In the meantime, the Romans hoped to gain success through sheer strength and weight of numbers, and they raised a new army of unprecedented size, estimated by some to be as large as 100,000 men, but more likely around 50–80,000.[51]
The Romans and allied legions resolved to confront Hannibal and marched southward to Apulia. They eventually found him on the left bank of the Aufidus River, and encamped six miles (9.7 km) away. On this occasion, the two armies were combined into one, the consuls having to alternate their command on a daily basis. Varro was in command on the first day, a man of reckless and hubristic nature (according to Livy) and determined to defeat Hannibal.[51] Hannibal capitalized on the eagerness of Varro and drew him into a trap by using an envelopment tactic. This eliminated the Roman numerical advantage by shrinking the combat area. Hannibal drew up his least reliable infantry in a semicircle in the center with the wings composed of the Gallic and Numidian horse.[51] The Roman legions forced their way through Hannibal's weak center, but the Libyan mercenaries on the wings, swung around by the movement, menaced their flanks. The onslaught of Hannibal's cavalry was irresistible. Hannibal's chief cavalry commander Maharbal led the mobile Numidian cavalry on the right, and they shattered the Roman cavalry opposing them. Hannibal's Iberian and Gallic heavy cavalry, led by Hanno on the left, defeated the Roman heavy cavalry, and then both the Carthaginian heavy cavalry and the Numidians attacked the legions from behind. As a result, the Roman army was hemmed in with no means of escape.
Due to these brilliant tactics, Hannibal managed to surround and destroy all but a small remnant of his enemy, despite his own inferior numbers. Depending upon the source, it is estimated that 50,000–70,000 Romans were killed or captured.[3] Among the dead were Roman Consul Lucius Aemilius Paullus, as well as two consuls for the preceding year, two quaestors, twenty-nine out of the forty-eight military tribunes, and an additional eighty senators (at a time when the Roman Senate was composed of no more than 300 men, this constituted 25%–30% of the governing body). This makes the battle one of the most catastrophic defeats in the history of Ancient Rome, and one of the bloodiest battles in all of human history (in terms of the number of lives lost within a single day).[51]
After Cannae, the Romans were very hesitant to confront Hannibal in pitched battle, preferring instead to weaken him by attrition, relying on their advantages of interior lines, supply, and manpower. As a result, Hannibal fought no more major battles in Italy for the rest of the war. It is believed that his refusal to bring the war to Rome itself was due to a lack of commitment from Carthage of men, money, and material — principally siege equipment. Whatever the reason, the choice prompted Maharbal to say, "Hannibal, you know how to gain a victory, but not how to use one."[52]

Hannibal counting the signet rings of Roman nobles killed during the battle, statue by Sébastien Slodtz, 1704, Louvre
As a result of this victory, many parts of Italy joined Hannibal's cause.[53] As Polybius notes, "How much more serious was the defeat of Cannae, than those that preceded it can be seen by the behavior of Rome's allies; before that fateful day, their loyalty remained unshaken, now it began to waver for the simple reason that they despaired of Roman Power."[54] During that same year, the Greek cities in Sicily were induced to revolt against Roman political control, while Macedonian King Philip V pledged his support to Hannibal – thus initiating the First Macedonian War against Rome. Hannibal also secured an alliance with newly appointed tyrant Hieronymus of Syracuse. It is often argued that, if Hannibal had received proper material reinforcements from Carthage, he might have succeeded with a direct attack upon Rome. Instead, he had to content himself with subduing the fortresses that still held out against him, and the only other notable event of 216 BC was the defection of certain Italian territories, including Capua, the second largest city of Italy, which Hannibal made his new base. However, only a few of the Italian city-states defected to him that he had expected to gain as allies.
Stalemate
The war in Italy settled into a strategic stalemate. The Romans used the attritional strategy that Fabius had taught them, and which, they finally realized, was the only feasible means of defeating Hannibal.[55] Indeed, Fabius received the name "Cunctator" ("the Delayer") because of his policy of not meeting Hannibal in open battle but through attrition.[56]
The Romans deprived Hannibal of a large-scale battle and instead assaulted his weakening army with multiple smaller armies in an attempt to both weary him and create unrest in his troops.[3] For the next few years, Hannibal was forced to sustain a scorched earth policy and obtain local provisions for protracted and ineffectual operations throughout southern Italy. His immediate objectives were reduced to minor operations centered mainly round the cities of Campania.
The forces detached to his lieutenants were generally unable to hold their own, and neither his home government nor his new ally Philip V of Macedon helped to make up his losses. His position in southern Italy, therefore, became increasingly difficult and his chance of ultimately conquering Rome grew ever more remote. Hannibal still won a number of notable victories: completely destroying two Roman armies in 212 BC, and killing two consuls (including the famed Marcus Claudius Marcellus) in a battle in 208 BC. However, Hannibal slowly began losing ground—inadequately supported by his Italian allies, abandoned by his government (either because of jealousy or simply because Carthage was overstretched), and unable to match Rome's resources. He was never able to bring about another grand decisive victory that could produce a lasting strategic change.
Carthaginian political will was embodied in the ruling oligarchy. There was a Carthaginian Senate, but the real power was with the inner "Council of 30 Nobles" and the board of judges from ruling families known as the "Hundred and Four". These two bodies came from the wealthy, commercial families of Carthage. Two political factions operated in Carthage: the war party, also known as the "Barcids" (Hannibal's family name); and the peace party led by Hanno II the Great. Hanno had been instrumental in denying Hannibal's requested reinforcements following the battle at Cannae.
Hannibal started the war without the full backing of Carthaginian oligarchy. His attack of Saguntum had presented the oligarchy with a choice of war with Rome or loss of prestige in Iberia. The oligarchy, not Hannibal, controlled the strategic resources of Carthage. Hannibal constantly sought reinforcements from either Iberia or North Africa. Hannibal's troops who were lost in combat were replaced with less well-trained and motivated mercenaries from Italy or Gaul. The commercial interests of the Carthaginian oligarchy dictated the reinforcement and supply of Iberia rather than Hannibal throughout the campaign.
Hannibal's retreat in Italy

Bust of Scipio Africanus from the Villa of the Papyri
In March 212 BC, Hannibal captured Tarentum in a surprise attack but he failed to obtain control of its harbour. The tide was slowly turning against him, and in favor of Rome.
The Roman consuls mounted a siege of Capua in 212 BC. Hannibal attacked them, forcing their withdrawal from Campania. He moved to Lucania and destroyed a 16,000-man Roman army at the Battle of the Silarus, with 15,000 Romans killed. Another opportunity presented itself soon after, a Roman army of 18,000 men being destroyed by Hannibal at the first battle of Herdonia with 16,000 Roman dead, freeing Apulia from the Romans for the year. The Roman consuls mounted another siege of Capua in 211 BC, conquering the city. Hannibal attempted to lift the siege with an assault on the Roman siege lines but failed. He marched on Rome to force the recall of the Roman armies. He drew off 15,000 Roman soldiers, but the siege continued and Capua fell. In 212 BC, Marcellus conquered Syracuse and the Romans destroyed the Carthaginian army in Sicily in 211–210 BC. In 210 BC, the Romans entered into an alliance with the Aetolian League to counter Philip V of Macedon. Philip, who attempted to exploit Rome's preoccupation in Italy to conquer Illyria, now found himself under attack from several sides at once and was quickly subdued by Rome and her Greek allies.
In 210 BC, Hannibal again proved his superiority in tactics by inflicting a severe defeat at the Battle of Herdonia (modern Ordona) in Apulia upon a proconsular army and, in 208 BC, destroyed a Roman force engaged in the siege of Locri at the Battle of Petelia. But with the loss of Tarentum in 209 BC and the gradual reconquest by the Romans of Samnium and Lucania, his hold on south Italy was almost lost. In 207 BC, he succeeded in making his way again into Apulia, where he waited to concert measures for a combined march upon Rome with his brother Hasdrubal Barca. On hearing, however, of his brother's defeat and death at the battle of the Metaurus, he retired to Calabria, where he maintained himself for the ensuing years. His brother's head had been cut off, carried across Italy, and tossed over the palisade of Hannibal's camp as a cold message of the iron-clad will of the Roman Republic. The combination of these events marked the end to Hannibal's success in Italy. With the failure of his brother Mago in Liguria (205–203 BC) and of his own negotiations with Phillip V, the last hope of recovering his ascendancy in Italy was lost. In 203 BC, after nearly fifteen years of fighting in Italy, and with the military fortunes of Carthage rapidly declining, Hannibal was recalled to Carthage to direct the defense of his native country against a Roman invasion under Scipio Africanus.
Conclusion of the Second Punic War (203–201 BC)
Return to Carthage

Final act of the Second Punic War with the battle of Zama (202 BC)
In 203 BC, Hannibal was recalled from Italy by the war party in Carthage. After leaving a record of his expedition engraved in Punic and Greek upon bronze tablets in the temple of Juno Lacinia at Crotona, he sailed back to Africa.[57] His arrival immediately restored the predominance of the war party, which placed him in command of a combined force of African levies and his mercenaries from Italy. In 202 BC, Hannibal met Scipio in a fruitless peace conference. Despite mutual admiration, negotiations floundered due to Roman allegations of "Punic Faith," referring to the breach of protocols that ended the First Punic War by the Carthaginian attack on Saguntum, and a Carthaginan attack on a stranded Roman fleet. Scipio and Carthage had worked out a peace plan, which was approved by Rome. The terms of the treaty were quite modest, but the war had been long for the Romans. Carthage could keep its African territory but would lose its overseas empire. Masinissa (Numidia) was to be independent. Also, Carthage was to reduce its fleet and pay a war indemnity. But Carthage then made a terrible blunder. Its long-suffering citizens had captured a stranded Roman fleet in the Gulf of Tunis and stripped it of supplies, an action that aggravated the faltering negotiations. Meanwhile, Hannibal, recalled from Italy by the Carthaginian Senate, had returned with his army. Fortified by both Hannibal and the supplies, the Carthaginians rebuffed the treaty and Roman protests. The decisive battle of Zama soon followed; the defeat removed Hannibal's air of invincibility.
Battle of Zama (202 BC)
Unlike most battles of the Second Punic War, at Zama, the Romans were superior in cavalry and the Carthaginians had the edge in infantry. This Roman cavalry superiority was due to the betrayal of Masinissa, who had earlier assisted Carthage in Iberia, but changed sides in 206 BC with the promise of land and due to his personal conflicts with Syphax, a Carthaginian ally. Although the aging Hannibal was suffering from mental exhaustion and deteriorating health after years of campaigning in Italy, the Carthaginians still had the advantage in numbers and were boosted by the presence of 80 war elephants.

Engraving of the Battle of Zama by Cornelis Cort, 1567. Note that Asian elephants are illustrated rather than the very small North African elephants used by Carthage.
The Roman cavalry won an early victory by swiftly routing the Carthaginian horse, and standard Roman tactics for limiting the effectiveness of the Carthaginian war elephants were successful, including playing trumpets to frighten the elephants into running into the Carthaginian lines. Some historians say that the elephants routed the Carthaginian cavalry and not the Romans, whilst others suggest that it was actually a tactical retreat planned by Hannibal.[58] Whatever the truth, the battle remained closely fought. At one point, it seemed that Hannibal was on the verge of victory, but Scipio was able to rally his men, and his cavalry, having routed the Carthaginian cavalry, attacked Hannibal's rear. This two-pronged attack caused the Carthaginian formation to collapse.
With their foremost general defeated, the Carthaginians had no choice but to surrender. Carthage lost approximately 20,000 troops with an additional 15,000 wounded. In contrast, the Romans suffered only 2,500 casualties. The last major battle of the Second Punic War resulted in a loss of respect for Hannibal by his fellow Carthaginians. The conditions of defeat were such that Carthage could no longer battle for Mediterranean supremacy.
Later career
Peacetime Carthage (200–196 BC)

A Carthaginian coin possibly depicting Hannibal as Hercules (i.e. Heracles)
Hannibal was still only 46 at the conclusion of the Second Punic War in 201 BC and soon showed that he could be a statesman as well as a soldier. Following the conclusion of a peace that left Carthage saddled with an indemnity of ten thousand talents, he was elected suffete, (chief magistrate) of the Carthiginian state.[59] After an audit confirmed Carthage had the resources to pay the indemnity without increasing taxation, Hannibal initiated a reorganization of state finances aimed at eliminating corruption and recovering embezzled funds.[60]
The principal beneficiaries of these financial peculations had been the oligarchs of the Hundred and Four.[61] In order to reduce the power of the oligarchs, Hannibal passed a law stipulating the Hundred and Four be chosen by direct election rather than co-option. He also used citizen support to change the term of office in the Hundred and Four from life to a year, with none permitted to "hold office for two consecutive years."[62][63]
Exile (after 195 BC)
Seven years after the victory of Zama, the Romans, alarmed by Carthage's renewed prosperity and suspicious that Hannibal had been in contact with Antiochus III of Syria, sent a delegation to Carthage alleging Hannibal was helping an enemy of Rome.[64] Aware that he had many enemies, not least of which due to his financial reforms eliminating opportunities for oligarchical graft, Hannibal fled into voluntary exile before the Romans could demand that Carthage surrender him into their custody.[65]
He journeyed first to Tyre, the mother city of Carthage, and then to Antioch, before he finally reached Ephesus, where he was honorably received by Antiochus. Livy states that the Seleucid king consulted Hannibal on the strategic concerns of making war on Rome. The Carthaginian general advised equipping a fleet and landing a body of troops in the south of Italy, offering to take command himself.[66] According to Cicero, while at the court of Antiochus, Hannibal attended a lecture by Phormio, a philosopher, that ranged through many topics. When Phormio finished a discourse on the duties of a general, Hannibal was asked his opinion. He replied, "I have seen during my life many old fools; but this one beats them all." Another story, according to Aulus Gellius, is that when Antiochus III showed off the gigantic and elaborately equipped army he had created to invade Greece to Hannibal, he asked him if they would be enough for the Roman Republic, to which Hannibal replied, "I think all this will be enough, yes, quite enough, for the Romans, even though they are most avaricious."[67] In 191 BC, the Romans under Manius Acilius Glabrio routed Antiochus at the battle of Thermopylae and obliged him to withdraw to Asia. The Romans followed up their success by attacking Antiochus in Anatolia and the Seleucid Empire was decisively defeated at the battle of Magnesia in 190 BC by Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus.
In 190 BC, Hannibal was placed in command of a Seleucid fleet but was defeated in the battle of the Eurymedon.[68] According to Strabo and Plutarch, Hannibal also received hospitality at the Armenian royal court of Artaxias I. The authors add an apocryphal story of how Hannibal planned and supervised the building of the new royal capital Artaxata.[69] Suspicious that Antiochus was prepared to surrender him to the Romans, Hannibal fled to Crete, but he soon went back to Anatolia and sought refuge with Prusias I of Bithynia, who was engaged in warfare with Rome's ally, King Eumenes II of Pergamon.[70] Hannibal went on to serve Prusias in this war. During one of the naval victories he gained over Eumenes, Hannibal had large pots filled with venomous snakes thrown onto Eumenes' ships.[71] Hannibal also went on to defeat Eumenes in two other battles on land.[72]
Death (183 to 181 BC)
At this stage, the Romans intervened and threatened Bithynia into giving up Hannibal.[73] Prusias agreed, but the general was determined not to fall into his enemy's hands. The precise year and cause of Hannibal's death are unknown. Pausanias wrote that Hannibal's death occurred after his finger was wounded by his drawn sword while mounting his horse, resulting in a fever and then his death three days later.[74] Juvenal asserts that his death was at Libyssa on the eastern shore of the Sea of Marmara, after having taken poison, which he had long carried about with him in a ring.[75] Before dying, he left behind a letter declaring, "Let us relieve the Romans from the anxiety they have so long experienced, since they think it tries their patience too much to wait for an old man's death".[76]
In his Annales, Titus Pomponius Atticus reports that Hannibal's death occurred in 183 BC,[77] and Livy implies the same. Polybius, who wrote nearest the event, gives 182 BC. Sulpicius Blitho[78] records the death under 181 BC.[77]
Legacy
Legacy to the ancient world
Hannibal caused great distress to many in Roman society. He became such a figure of terror that whenever disaster struck, the Roman senators would exclaim "Hannibal ante portas" ("Hannibal is at the gates!") to express their fear or anxiety. This famous Latin phrase became a common expression that is often still used when a client arrives through the door or when one is faced with calamity.[79]
The works of Roman writers such as Livy (64 or 59 BC – AD 12 or 17), Frontinus (c. 40 – 103 AD), and Juvenal (1st to 2nd century AD) show a grudging admiration for Hannibal. The Romans even built statues of the Carthaginian in the very streets of Rome to advertise their defeat of such a worthy adversary.[80][need quotation to verify] It is plausible to suggest that Hannibal engendered the greatest fear Rome had towards an enemy. Nevertheless, the Romans grimly refused to admit the possibility of defeat and rejected all overtures for peace; they even refused to accept the ransom of prisoners after Cannae.[81]
During the war there are no reports of revolutions among the Roman citizens, no factions within the Senate desiring peace, no pro-Carthaginian Roman turncoats, no coups.[82][83] Indeed, throughout the war Roman aristocrats ferociously competed with each other for positions of command to fight against Rome's most dangerous enemy. Hannibal's military genius was not enough to really disturb the Roman political process and the collective political and military capacity of the Roman people. As Lazenby states,
It says volumes, too, for their political maturity and respect for constitutional forms that the complicated machinery of government continued to function even amidst disaster—there are few states in the ancient world in which a general who had lost a battle like Cannae would have dared to remain, let alone would have continued to be treated respectfully as head of state.[84]
According to the historian Livy, the Romans feared Hannibal's military genius, and during Hannibal's march against Rome in 211 BC
"a messenger who had travelled from Fregellae for a day and a night without stopping created great alarm in Rome, and the excitement was increased by people running about the City with wildly exaggerated accounts of the news he had brought. The wailing cry of the matrons was heard everywhere, not only in private houses but even in the temples. Here they knelt and swept the temple-floors with their dishevelled hair and lifted up their hands to heaven in piteous entreaty to the gods that they would deliver the City of Rome out of the hands of the enemy and preserve its mothers and children from injury and outrage."[85]
In the Senate the news was "received with varying feelings as men's temperaments differed,"[85] so it was decided to keep Capua under siege, but to send 15,000 infantry and 1,000 cavalry as reinforcements to Rome.[85]
According to Livy, the land occupied by Hannibal's army outside Rome in 211 BC was sold at the very time of its occupation and for the same price.[86] This may not be true, but as Lazenby states, "could well be, exemplifying as it does not only the supreme confidence felt by the Romans in ultimate victory, but also the way in which something like normal life continued."[87] After Cannae the Romans showed a considerable steadfastness in adversity. An undeniable proof of Rome's confidence is demonstrated by the fact that after the Cannae disaster she was left virtually defenseless, but the Senate still chose not to withdraw a single garrison from an overseas province to strengthen the city. In fact, they were reinforced and the campaigns there maintained until victory was secured; beginning first in Sicily under the direction of Claudius Marcellus, and later in Hispania under Scipio Africanus.[88][89] Although the long-term consequences of Hannibal's war are debatable, this war was undeniably Rome's "finest hour".[90][91][need quotation to verify]
Most of the sources available to historians about Hannibal are from Romans. They considered him the greatest enemy Rome had ever faced. Livy gives us the idea that Hannibal was extremely cruel. Even Cicero, when he talked of Rome and its two great enemies, spoke of the "honourable" Pyrrhus and the "cruel" Hannibal. Yet a different picture sometimes emerges. When Hannibal's successes had brought about the death of two Roman consuls, he vainly searched for the body of Gaius Flaminius on the shores of Lake Trasimene, held ceremonial rituals in recognition of Lucius Aemilius Paullus, and sent Marcellus' ashes back to his family in Rome. Any bias attributed to Polybius, however, is more troublesome. Ronald Mellor considered the Greek scholar a loyal partisan of Scipio Aemilianus,[92] while H. Ormerod does not view him as an 'altogether unprejudiced witness' when it came to his pet peeves, the Aetolians, the Carthaginians, and the Cretans.[93] Nonetheless, Polybius did recognize that the reputation for cruelty the Romans attached to Hannibal Barca might in reality have been due to mistaking him for one of his officers, Hannibal Monomachus.[94]
Military history

The material of legend, in Snow Storm: Hannibal and his Army Crossing the Alps, J. M. W. Turner envelops Hannibal's crossing of the Alps in Romantic atmosphere.
Hannibal is generally regarded as one of the best military strategists and tacticians of all time, the double envelopment at Cannae an enduring legacy of tactical brilliance. According to Appian, several years after the Second Punic War, Hannibal served as a political advisor in the Seleucid Kingdom and Scipio was sent there on a diplomatic mission from Rome.
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
It is said that at one of their meetings in the gymnasium Scipio and Hannibal had a conversation on the subject of generalship, in the presence of a number of bystanders, and that Scipio asked Hannibal whom he considered the greatest general, to which the latter replied, "Alexander of Macedonia".
To this Scipio assented since he also yielded the first place to Alexander. Then he asked Hannibal whom he placed next, and he replied, "Pyrrhus of Epirus", because he considered boldness the first qualification of a general; "for it would not be possible", he said, "to find two kings more enterprising than these".
Scipio was rather nettled by this, but nevertheless he asked Hannibal to whom he would give the third place, expecting that at least the third would be assigned to him; but Hannibal replied, "to myself; for when I was a young man I conquered Hispania and crossed the Alps with an army, the first after Hercules."
As Scipio saw that he was likely to prolong his self-laudation he said, laughing, "where would you place yourself, Hannibal, if you had not been defeated by me?" Hannibal, now perceiving his jealousy, replied, "in that case I should have put myself before Alexander". Thus Hannibal continued his self-laudation, but flattered Scipio in an indirect manner by suggesting that he had conquered one who was the superior of Alexander.
At the end of this conversation Hannibal invited Scipio to be his guest, and Scipio replied that he would be so gladly if Hannibal were not living with Antiochus, who was held in suspicion by the Romans. Thus did they, in a manner worthy of great commanders, cast aside their enmity at the end of their wars.[95]
Military academies all over the world continue to study Hannibal's exploits, especially his victory at Cannae.[citation needed]

Hannibal's celebrated feat in crossing the Alps with war elephants passed into European legend: detail of a fresco by Jacopo Ripanda, ca. 1510, Capitoline Museums, Rome.
Maximilian Otto Bismarck Caspari, in his article in the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, praises Hannibal in these words:
As to the transcendent military genius of Hannibal there cannot be two opinions. The man who for fifteen years could hold his ground in a hostile country against several powerful armies and a succession of able generals must have been a commander and a tactician of supreme capacity. In the use of strategies and ambuscades he certainly surpassed all other generals of antiquity. Wonderful as his achievements were, we must marvel the more when we take into account the grudging support he received from Carthage. As his veterans melted away, he had to organize fresh levies on the spot. We never hear of a mutiny in his army, composed though it was of North Africans, Iberians and Gauls. Again, all we know of him comes for the most part from hostile sources. The Romans feared and hated him so much that they could not do him justice. Livy speaks of his great qualities, but he adds that his vices were equally great, among which he singles out his more than Punic perfidy and an inhuman cruelty. For the first there would seem to be no further justification than that he was consummately skillful in the use of ambuscades. For the latter there is, we believe, no more ground than that at certain crises he acted in the general spirit of ancient warfare. Sometimes he contrasts most favorably with his enemy. No such brutality stains his name as that perpetrated by Claudius Nero on the vanquished Hasdrubal Barca. Polybius merely says that he was accused of cruelty by the Romans and of avarice by the Carthaginians. He had indeed bitter enemies, and his life was one continuous struggle against destiny. For steadfastness of purpose, for organizing capacity and a mastery of military science he has perhaps never had an equal.[96]
Even the Roman chroniclers acknowledged Hannibal's supreme military leadership, writing that, "he never required others to do what he could and would not do himself".[97]
According to Polybius 23, 13, p. 423:
It is a remarkable and very cogent proof of Hannibal's having been by nature a real leader and far superior to anyone else in statesmanship, that though he spent seventeen years in the field, passed through so many barbarous countries, and employed to aid him in desperate and extraordinary enterprises numbers of men of different nations and languages, no one ever dreamt of conspiring against him, nor was he ever deserted by those who had once joined him or submitted to him.

A bust of Hannibal, 17th century, Museum of Antiquities (Saskatoon)
Count Alfred von Schlieffen developed his eponymously titled "Schlieffen Plan" (1905/1906) from his military studies, with a particularly heavy emphasis on the envelopment technique which Hannibal employed to surround and destroy the Roman army in the battle of Cannae.[98][99]George S. Patton believed himself a reincarnation of Hannibal as well as of many other people, including a Roman legionary and a Napoleonic soldier.[100][101]Norman Schwarzkopf Jr., the commander of the Coalition of the Gulf War, claimed, "The technology of war may change, the sophistication of weapons certainly changes. But those same principles of war that applied to the days of Hannibal apply today."[102]
According to the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge,
Hannibal excelled as a tactician. No battle in history is a finer sample of tactics than Cannae. But he was yet greater in logistics and strategy. No captain ever marched to and fro among so many armies of troops superior to his own numbers and material as fearlessly and skillfully as he. No man ever held his own so long or so ably against such odds. Constantly overmatched by better soldiers, led by generals always respectable, often of great ability, he yet defied all their efforts to drive him from Italy, for half a generation. Excepting in the case of Alexander, and some few isolated instances, all wars up to the Second Punic War, had been decided largely, if not entirely, by battle-tactics. Strategic ability had been comprehended only on a minor scale. Armies had marched towards each other, had fought in parallel order, and the conqueror had imposed terms on his opponent. Any variation from this rule consisted in ambuscades or other stratagems. That war could be waged by avoiding in lieu of seeking battle; that the results of a victory could be earned by attacks upon the enemy's communications, by flank-maneuvers, by seizing positions from which safely to threaten him in case he moved, and by other devices of strategy, was not understood... [However] For the first time in the history of war, we see two contending generals avoiding each other, occupying impregnable camps on heights, marching about each other's flanks to seize cities or supplies in their rear, harassing each other with small-war, and rarely venturing on a battle which might prove a fatal disaster—all with a well-conceived purpose of placing his opponent at a strategic disadvantage... That it did so was due to the teaching of Hannibal.[3]
Timeline
| Timeline of Hannibal's life (248 BC–c. 183 BC) |
|---|
 |
See also
Other Hannibals in Carthaginian history- Military of Carthage
- Alaric I
- Arminius
- Attila
- Bato (Daesitiate chieftain)
- Boiorix
- Brennus (4th century BC)
- Mithridates VI of Pontus
- Odoacer
- Gaiseric
- Spartacus
- Theodoric the Great
Notes
^ See death below.
References
Citations
^ "Plutarch, and when asked what his choices would be if he had beaten Scipio, he replied that he would be the best of them all" Life of Titus Flamininus 21.3–4.
^ Plutarch, Life of Pyrrhus 8.2.
^ abcde Ayrault Dodge, Theodore (1995). Hannibal: A History of the Art of War Among the Carthaginians and Romans Down to the Battle of Pydna, 168 BC. Da Capo Press..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Huss (1985), p. 565.
^ Brown, John Pairman. 2000. Israel and Hellas: Sacred institutions with Roman counterparts. P.126–128
^ ab Benz, Franz L. 1982. Personal Names in the Phoenician and Punic Inscriptions. P.313-314
^ ab Baier, Thomas. 2004. Studien zu Plautus' Poenulus. P.174
^ Friedrich, Johannes, Wolfgang Röllig, Maria Giulia Amadasi, and Werner R. Mayer. 1999. Phönizisch-Punische Grammatik. P.53.
^ Sullivan, Robert Joseph (1877), A Dictionary of the English Language, p. 489.
^ S. Lancel, Hannibal p.6.
^ Ameling, Walter Karthago: Studien zu Militär, Staat und Gesellschaft pp. 81–2.
^ Sylloge Nummorum Graecorum, Great Britain, Volume IX, British Museum, Part 2: Spain, London, 2002, n° 102.
^ Lancel, S. Hannibal p.6.
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.91.
^ Reverse Spins Patton, the Second Coming of Hannibal.
^ Hilowitz, Beverley (1974). A Horizon guide: great historic places of Europe. American Heritage Pub. Co., p. 119.
ISBN 0-07-028915-8
^ "Hamilcar Barca". Retrieved 6 June 2011.
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.94.
^ "The History of Rome: Vol III"., by Livy
^ "The History of Rome: Vol III"., by Livy
^ "The History of Rome: Vol III"., by Livy
^ Silius Italicus, Punica, III, 97
^ Picard, Gilbert Charles(1967), Hannibal p. 119
^ Silius Italicus, Punica, III, 63-64
^ Dodge, Theodore Ayrault (2004). Hannibal: A History of the Art of War Among the Carthaginians and Romans Down to the Battle of Pydna, 168 B.C., with a Detailed Account of the Second Punic War. Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-81362-7., page 143
^ Hoyos, D. Hannibal's Dynasty: Power and Politics in the Western Mediterranean, 247–183 BC, pp. 89–91, 2003
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.112-113.
^ "The History of Rome: Vol III"., by Livy
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.113.
^ "The History of Rome: Vol III"., by Livy
^ Fagan, Garret G. "The History of Ancient Rome". Lecture 13: "The Second Punic War". Teaching Company, "Great Courses" series.
^ Lancel, Serge (1999). Hannibal. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-631-21848-7., p. 225
^ Prevas, John (1 March 2009). Hannibal Crosses the Alps: The Invasion of Italy and the Punic Wars. Perseus Books Group. ISBN 978-0-7867-3121-3., p. 86
^ Mahaney, W. C. (2008). Hannibal's Odyssey: Environmental Background to the Alpine Invasion of Italia. Gorgias Press. ISBN 978-1-59333-951-7., page 221
^ Lancel, Serge (1999). Hannibal. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-631-21848-7., p. 60]
^ Montgenèvre: Peter Connolly, Hannibal and the Enemies of Rome (1978); (extensive summary); Col de la Traversette: Gavin de Beer, Alps and Elephants and Napoleon III; Mahaney 2008, "Hannibal's Odyssey; Environmental Background to the Alpine Invasion of Italia"; Mont Cenis: Denis Proctor, Hannibal's March in History. Other theories include the Col de Clapier (Serge Lancel, Hannibal (1995) and the Col du Petit Saint Bernard (Barthold Niebuhr).
^ McMenamin, M. (2012). "Depiction of the Alps on Punic coins from Campania, Italy". Numismatics International Bulletin. 41 (1–2): 30–33.
^ Boser, Ulrich (2007). "Hiking with Hannibal". Archaeology. 60 (1): 36–41.
^ Livy History of Rome book21,36
^ Livy History of Rome, Book 21 sections 32–36
^ Mahaney, W.C., et al., 2009. "The Traversette rockfall: geomorphological reconstruction and importance in interpreting classical history." Archaeometry, v. 52, no. 1, pp. 156–172.
^ S. Lancel, Hannibal (1995; English translation 1999) page 60.
^ ab Dodge, Theodore. Hannibal. Cambridge Massachusetts: De Capo Press, 1891
ISBN 0-306-81362-9
^ Polybius, Histories, Book III, 77
^ John Selby Watson; Marcus Junianus; Justinus, Cornelius; Nepos, Eutropius (1853). Justin, Cornelius Nepos, and Eutropius: Literally Translated, with Notes. H. G. Bohn. p. 420. Retrieved 23 July 2008.
^ Polybius, Histories, Book III, p74
^ Liddell Hart, B. H., Strategy, New York City, New York, Penguin Group, 1967
^ USAWC Comparing Strategies of the 2nd Punic War by James Parker. View as HTML
^ Goldsworthy, Adrian K. The Roman Army at War 100 BC — AD 200, New York
^ "Internet Ancient History Sourcebook".
^ abcd Cottrell, Leonard, Enemy of Rome, Evans Bros, 1965,
ISBN 0-237-44320-1
^ Prevas, John, Hannibal Crosses the Alps, p. xv
^ Chaplin, Jane Dunbar, Livy's Exemplary History, p. 66
^ Polybius, The Histories of Polybius, 2 Vols., trans. Evelyn S. Shuckburgh (London: Macmillan, 1889), I. 264–275.
^ Prevas, John, Hannibal Crosses the Alps: The Invasion of Italy and the Second Punic War, p. 200
^ Pliny the Elder (2005), The Elder Pliny on the Human Animal: Human History Book 7: Natural History, translated by Beagon, Mary, Oxford University Press, p. 361
^ "28.46". Gutenberg.org. 11 June 2004. Retrieved 6 June 2013.
^ Scullard, H.H. Scipio Africanus: Soldier and Politician, p. 150, 1970. Gabriel, Richard. Scipio Africanus: Rome's Greatest General, p. 192, 2008
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.291.
^ "The History of Rome: Vol V"., by Livy
^ "The History of Rome: Vol V"., by Livy
^ "The History of Rome: Vol V"., by Livy
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.291.
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.296.
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.296.
^ "The History of Rome: Vol V"., by Livy
^ Aulus Gellius. Noctes Atticae, book V. v. 5. "Satis, plane satis esse credo Romanis haec omnia, etiamsi avarissimi sunt."
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.298.
^ Bournoutian, George A. (2006). A Concise History of the Armenian People: From Ancient Times to the Present. Costa Mesa, CA: Mazda, p. 29.
ISBN 1-56859-141-1.
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.299.
^ Cornelius Nepos, Hannibal 10 and 11.
^ Cornelius Nepos, Hannibal 12.
^ Cornelius Nepos, Hannibal 12.
^ Pausanias. "Description of Greece, 8.11.11". Perseus Digital Library. Retrieved 10 April 2016.
^ Cornelius Nepos, Hannibal 12.5; Juvenal, Satires X.164
^ Mellor, Ronald (1999). The Roman historians. Routledge. p. 70. ISBN 978-0-415-11773-9.
^ ab Cornelius Nepos, Hannibal 13.1
^ An otherwise unknown author; see The Fragments of the Roman Historians: Introduction. Vol. 1. Oxford University Press. 2013. ISBN 978-0-199-27705-6., page 429]
^
Alan Emrich, Practical Latin Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Holland, Rome and her Enemies 8
^ Livy, The War With Hannibal 22.61
^ Lazenby, Hannibal's War 237–8
^
Goldsworthy, The Fall of Carthage 315
^
J. F. Lazenby, The Hannibalic War, 254
^ abc
"Livy's History of Rome". Mcadams.posc.mu.edu. Retrieved 6 June 2013.
^ Livy, The War with Hannibal, 26.11
^ J.F. Lazenby, The Hannibalic War, p. 254
^ Bagnall, The Punic Wars 203
^ Lazenby, Hannibal's War 235
^ Lazenby Hannibal's War 254
^
Goldsworthy, Adrian (2012-08-30). The Fall of Carthage: The Punic Wars 265-146BC. Hachette UK (published 2012). p. 366–367. ISBN 9781780223063. Retrieved 2018-05-15.
^ Mellor, Ronald J. The Historians of Ancient Rome
^ Omerod, H. Piracy in the Ancient World, p.141
^ De Beer, Sir Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy p.111.
^ Appian, History of the Syrian Wars, §10 and §11 at Livius.org
^ Caspari, M.O.B. (1911). "Hannibal (general)". In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Caspari, M.O.B. (1911). "Hannibal (general)". In Chisholm, Hugh. Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
^ Hannibal Archived 1 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine. at CarpeNoctem.tv
^ Daly, Gregory (2003). Cannae: The Experience of Battle in the Second Punic War. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-32743-5., p. x
^ Cottrell, Leonard (1992). Hannibal: Enemy of Rome. Perseus Books Group. ISBN 978-0-306-80498-4., p. 134
^ "Any man who thinks he is the reincarnation of Hannibal or some such isn't quite possessed of all his buttons", quoted by D'Este, Carlo (1996). Patton: Genius for War, A. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-06-092762-2., p. 815
^ Hirshson, Stanley, General Patton: A Soldier's Life, p. 163
^ Carlton, James, The Military Quotation Book, New York City, New York, Thomas Dunne Books, 2002
Bibliography
Huss, Werner (1985), Geschichte der Karthager, Munich: C.H. Beck. (in German)
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Hannibal (general)". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Hannibal (general)". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Baker, George P. (1929). Hannibal. New York: Dodd, Mead.
Bickerman, Elias J. (1952). "Hannibal's Covenant". American Journal of Philology. 73 (1): 1–23. doi:10.2307/292232. JSTOR 292232.
Bradford, Ernle; Scullard, H.H. (1981). Hannibal. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-007064-6.
Caven, Brian (1980). The Punic Wars. New York: St. Martin's Press. ISBN 978-0-312-65580-8.
Cottrell, Leonard (1992). Hannibal : enemy of Rome. New York: Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-80498-4.
Daly, Gregory (2002). Cannae : the experience of battle in the second Punic War. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-32743-5.
De Beer, Gavin (1969). Hannibal: Challenging Rome's Supremacy. New York: Viking Press.
Garland, Robert (2010). Hannibal. London: Bristol Classical Press. ISBN 978-1-85399-725-9.
Delbrück, Hans (1990). Warfare in antiquity. Walter J. Renfroe, trans. Lincoln: Univ. of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-9199-7.
Dodge, Theodore Ayrault (1891). Hannibal. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Hoyos, Dexter (2003). Hannibal's dynasty power and politics in the western Mediterranean, 247-183 BC. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-41782-9.
Hoyos, Dexter (2008). Hannibal : Rome's greatest enemy. Exeter: Bristol Phoenix Press. ISBN 978-1-904675-46-4.
Lamb, Harold (1958). Hannibal: one man against Rome. Garden City, NY: Doubleday.
Lancel, Serge Lancel (1999). Hannibal. Antonia Nevill, trans. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-21848-7.
Livy (1972). Radice, Betty, ed. The war with Hannibal : books XXI-XXX of the History of Rome from its foundation. Aubrey De Sélincourt, trans. Harmondsworth: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-044145-1. Archived from the original on 16 February 2011.
Livy (2006). Hannibal's war : books twenty-one to thirty. J. C. Yardley, trans. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press. ISBN 978-0-19-283159-0.
- MacDonald, Eve. Hannibal: A Hellenistic Life (Yale UP, 2015) online review
Mahaney, William (2008). Hannibal's odyssey: environmental background to the alpine invasion of Italia. Piscataway, NJ: Gorgias Press. ISBN 978-1-59333-951-7.
Prevas, John (2001). Hannibal crosses the Alps : the invasion of Italy and the Punic Wars. Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-81070-1.
Toynbee, Arnold (1965). Hannibal's Legacy. London: Oxford University Press.
Mark, Joshua. "The Price of Greed: Hannibal's Betrayal by Carthage". Ancient History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 20 December 2011.
External links
Library resources about Hannibal |
|
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Hannibal |
- Life of Hannibal by Cornelius Nepos at Perseus Digital Library
- History Blog: Hannibal at Tips.FM
- The Biography of Hannibal
Hannibal by Jacob Abbott
- Hannibal's life by Cornelius Nepos, Latin transcription and translation to German
- The History of Hannibal
- Hannibal at FactBehindFiction.com
- Hannibal - Barcelona to Rome at www.bikeodyssey.cc
- Hannibal Barca Association - https://www.hannibal-le-carthaginois.com

