Neural circuit

Anatomy of a multipolar neuron
A neural circuit, is a population of neurons interconnected by synapses to carry out a specific function when activated.[1] Neural circuits interconnect to one another to form large scale brain networks.[2] Biological neural networks have inspired the design of artificial neural networks.
Contents
1 Early study
2 Connections between neurons
3 Circuitry
4 Study methods
5 Clinical significance
6 See also
7 References
8 Further reading
9 External links
Early study
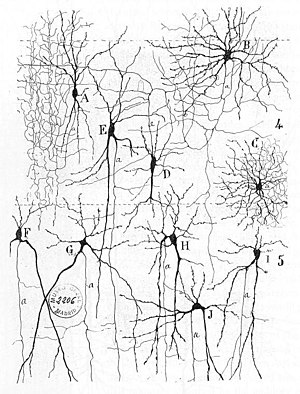
From "Texture of the Nervous System of Man and the Vertebrates" by Santiago Ramón y Cajal. The figure illustrates the diversity of neuronal morphologies in the auditory cortex.
Early treatments of neural networks can be found in Herbert Spencer's Principles of Psychology, 3rd edition (1872), Theodor Meynert's Psychiatry (1884), William James' Principles of Psychology (1890), and Sigmund Freud's Project for a Scientific Psychology (composed 1895).[3] The first rule of neuronal learning was described by Hebb in 1949, in the Hebbian theory. Thus, Hebbian pairing of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection and therefore either facilitate or inhibit signal transmission. In 1959, the neuroscientists, Warren Sturgis McCulloch and Walter Pitts published the first works on the processing of neural networks.[4] They showed theoretically that networks of artificial neurons could implement logical, arithmetic, and symbolic functions. Simplified models of biological neurons were set up, now usually called perceptrons or artificial neurons. These simple models accounted for neural summation (i.e., potentials at the post-synaptic membrane will summate in the cell body). Later models also provided for excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission.
Connections between neurons
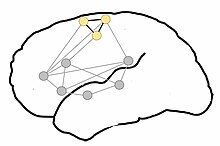
Proposed organization of motor-semantic neural circuits for action language comprehension. Gray dots represent areas of language comprehension, creating a network for comprehending all language. The semantic circuit of the motor system, particularly the motor representation of the legs (yellow dots), is incorporated when leg-related words are comprehended. Adapted from Shebani et al. (2013).
The connections between neurons in the brain are much more complex than those of the artificial neurons used in the connectionist neural computing models of artificial neural networks. The basic kinds of connections between neurons are synapses, chemical and electrical synapses.
The establishment of synapses enables the connection of neurons into millions of overlapping, and interlinking neural circuits. Neurexins are central to this process.[5]
One principle by which neurons work is neural summation – potentials at the postsynaptic membrane will sum up in the cell body. If the depolarization of the neuron at the axon goes above threshold an action potential will occur that travels down the axon to the terminal endings to transmit a signal to other neurons. Excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission is realized mostly by inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) and excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs).
On the electrophysiological level, there are various phenomena which alter the response characteristics of individual synapses (called synaptic plasticity) and individual neurons (intrinsic plasticity). These are often divided into short-term plasticity and long-term plasticity. Long-term synaptic plasticity is often contended to be the most likely memory substrate. Usually the term "neuroplasticity" refers to changes in the brain that are caused by activity or experience.
Connections display temporal and spatial characteristics. Temporal characteristics refer to the continuously modified activity-dependent efficacy of synaptic transmission, called spike-timing-dependent plasticity. It has been observed in several studies that the synaptic efficacy of this transmission can undergo short-term increase (called facilitation) or decrease (depression) according to the activity of the presynaptic neuron. The induction of long-term changes in synaptic efficacy, by long-term potentiation (LTP) or depression (LTD), depends strongly on the relative timing of the onset of the excitatory postsynaptic potential and the postsynaptic action potential. LTP is induced by a series of action potentials which cause a variety of biochemical responses. Eventually, the reactions cause the expression of new receptors on the cellular membranes of the postsynaptic neurons or increase the efficacy of the existing receptors through phosphorylation.
Backpropagating action potentials cannot occur because after an action potential travels down a given segment of the axon, the m gates on voltage-gated sodium channels close, thus blocking any transient opening of the h gate from causing a change in the intracellular sodium ion (Na+) concentration, and preventing the generation of an action potential back towards the cell body. In some cells, however, neural backpropagation does occur through the dendritic branching and may have important effects on synaptic plasticity and computation.
A neuron in the brain requires a single signal to a neuromuscular junction to stimulate contraction of the postsynaptic muscle cell. In the spinal cord, however, at least 75 afferent neurons are required to produce firing. This picture is further complicated by variation in time constant between neurons, as some cells can experience their EPSPs over a wider period of time than others.
While in synapses in the developing brain synaptic depression has been particularly widely observed it has been speculated that it changes to facilitation in adult brains.
Circuitry
An example of a neural circuit is the trisynaptic circuit in the hippocampus. Another is the Papez circuit linking the hypothalamus to the limbic lobe. There are several neural circuits in the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. These circuits carry information between the cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus, and back to the cortex. The largest structure within the basal ganglia, the striatum, is seen as having its own internal microcircuitry.[6]
Neural circuits in the spinal cord called central pattern generators are responsible for controlling motor instructions involved in rhythmic behaviours. Rhythmic behaviours include walking, urination, and ejaculation. The central pattern generators are made up of different groups of spinal interneurons.[7]
Study methods
Different neuroimaging techniques have been developed to investigate the activity of neural circuits and networks. The use of "brain scanners" or functional neuroimaging to investigate the structure or function of the brain is common, either as simply a way of better assessing brain injury with high resolution pictures, or by examining the relative activations of different brain areas. Such technologies may include functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), brain positron emission tomography (brain PET), and computed axial tomography (CAT) scans. Functional neuroimaging uses specific brain imaging technologies to take scans from the brain, usually when a person is doing a particular task, in an attempt to understand how the activation of particular brain areas is related to the task. In functional neuroimaging, especially fMRI, which measures hemodynamic activity (using BOLD-contrast imaging) which is closely linked to neural activity, PET, and electroencephalography (EEG) is used.
Connectionist models serve as a test platform for different hypotheses of representation, information processing, and signal transmission. Lesioning studies in such models, e.g. artificial neural networks, where parts of the nodes are deliberately destroyed to see how the network performs, can also yield important insights in the working of several cell assemblies. Similarly, simulations of dysfunctional neurotransmitters in neurological conditions (e.g., dopamine in the basal ganglia of Parkinson's patients) can yield insights into the underlying mechanisms for patterns of cognitive deficits observed in the particular patient group. Predictions from these models can be tested in patients or via pharmacological manipulations, and these studies can in turn be used to inform the models, making the process iterative.
Clinical significance
Sometimes neural circuitries can become pathological and cause problems such as in Parkinson's disease when the basal ganglia are involved.[8] Problems in the Papez circuit can also give rise to a number of neurodegenerative disorders including Parkinson's.
See also
- Feedback
- List of regions in the human brain
- Network science
- Neural coding
- Neural engineering
- Neural oscillation
- Pulse-coupled networks
References
^ Purves, Dale (2011). Neuroscience (5th ed.). Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer. p. 507. ISBN 9780878936953..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Neural Circuits | Centre of Excellence for Integrative Brain Function". Centre of Excellence for Integrative Brain Function. 13 June 2016. Retrieved 4 June 2018.
^ Michael S. C. Thomas; James L. McClelland. "Connectionist models of cognition" (PDF). Stanford University.
^ J. Y. Lettvin; H. R. Maturana; W. S. McCulloch; W. H. Pitts (1959), "What the frog's eye tells the frog's brain.", Proc. Inst. Radio Engr. (47), pp. 1940–1951
^ Südhof, TC (2 November 2017). "Synaptic Neurexin Complexes: A Molecular Code for the Logic of Neural Circuits". Cell. 171 (4): 745–769. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.024. PMC 5694349. PMID 29100073.
^ Stocco, Andrea; Lebiere, Christian; Anderson, John R. (2010). "Conditional Routing of Information to the Cortex: A Model of the Basal Ganglia's Role in Cognitive Coordination". Psychological Review. 117 (2): 541–74. doi:10.1037/a0019077. PMC 3064519. PMID 20438237.
^ Guertin, PA (2012). "Central pattern generator for locomotion: anatomical, physiological, and pathophysiological considerations". Frontiers in Neurology. 3: 183. doi:10.3389/fneur.2012.00183. PMC 3567435. PMID 23403923.
^ French, IT; Muthusamy, KA (2018). "A Review of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus in Parkinson's Disease". Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 10: 99. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2018.00099. PMC 5933166. PMID 29755338.
Further reading
Intrinsic plasticity Robert H. Cudmore, Niraj S. Desai Scholarpedia 3(2):1363. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.1363
External links
- Comparison of Neural Networks in the Brain and Artificial Neural Networks
- Lecture notes at MIT OpenCourseWare
- Computation in the Brain
Biological Neural Network Toolbox - A free Matlab toolbox for simulating networks of several different types of neurons
WormWeb.org: Interactive Visualization of the C. elegans Neural Network - C. elegans, a nematode with 302 neurons, is the only organism for whom the entire neural network has been uncovered. Use this site to browse through the network and to search for paths between any 2 neurons.
Introduction to Neurons and Neuronal Networks, Neuroscience Online (electronic neuroscience textbook)- Delaying Pulse Networks (Wave Interference Networks)