Boston
Boston, Massachusetts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
City | |||
| City of Boston | |||
    Clockwise from top: Downtown; Massachusetts State House; Back Bay and the Charles River; Fenway Park | |||
| |||
| Nickname(s): See Boston nicknames | |||
| Motto(s): Sicut patribus sit Deus nobis (Latin) "As God was with our fathers, so may He be with us" | |||
Interactive map of Boston | |||
| Coordinates: 42°21′29″N 71°03′49″W / 42.35806°N 71.06361°W / 42.35806; -71.06361Coordinates: 42°21′29″N 71°03′49″W / 42.35806°N 71.06361°W / 42.35806; -71.06361 | |||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| County | |||
| Historic countries | |||
| Historic colonies | Massachusetts Bay Colony in the Province of Massachusetts Bay | ||
| Settled (town) | September 7, 1630 (date of naming, Old Style)[a] | ||
| Incorporated (city) | March 4, 1822 | ||
| Named for | Boston, Lincolnshire | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Strong mayor / Council | ||
| • Mayor | Marty Walsh (D) | ||
| • Council | Boston City Council | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 89.63 sq mi (232.14 km2) | ||
| • Land | 48.42 sq mi (125.41 km2) | ||
| • Water | 41.21 sq mi (106.73 km2) | ||
| • Urban | 1,770 sq mi (4,600 km2) | ||
| • Metro | 4,500 sq mi (11,700 km2) | ||
| • CSA | 10,600 sq mi (27,600 km2) | ||
| Elevation | 141 ft (43 m) | ||
| Population (2010)[2][3][4][5][6] | |||
| • City | 617,594 | ||
| • Estimate (2017)[3] | 685,094 | ||
| • Rank | 21st, U.S. as of 2017[update] incorporated places estimate | ||
| • Density | 14,149/sq mi (5,463/km2) | ||
| • Urban | 4,180,000 (US: 10th) | ||
| • Metro | 4,628,910 (US: 10th)[1] | ||
| • CSA | 8,041,303 (US: 6th) | ||
| • Demonym | Bostonian | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| ZIP Codes | 53 ZIP codes[7]
| ||
| Area codes | 617 and 857 | ||
| FIPS code | 25-07000 | ||
GNIS feature ID | 0617565 | ||
| Primary Airport | Logan International Airport | ||
| Interstates | |||
| Commuter Rail | MBTA Commuter Rail | ||
| Rapid Transit | MBTA Subway | ||
| Website | Boston.gov | ||
Boston is the capital and most populous municipality[8] of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city proper covers 48 square miles (124 km2) with an estimated population of 685,094 in 2017,[3] making it also the most populous city in the New England region.[2] Boston is the seat of Suffolk County as well, although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999.[9] The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest such area in the country.[10] As a combined statistical area (CSA), this wider commuting region is home to some 8.2 million people, making it the sixth-largest in the United States.[11]
Boston is one of the oldest cities in the United States, founded on the Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by Puritan settlers from England.[12][13] It was the scene of several key events of the American Revolution, such as the Boston Massacre, the Boston Tea Party, the Battle of Bunker Hill, and the Siege of Boston. Upon gaining U.S. independence from Great Britain, it continued to be an important port and manufacturing hub as well as a center for education and culture.[14][15] The city has expanded beyond the original peninsula through land reclamation and municipal annexation. Its rich history attracts many tourists, with Faneuil Hall alone drawing more than 20 million visitors per year.[16] Boston's many firsts include the United States' first public park (Boston Common, 1634), first public or state school (Boston Latin School, 1635)[17] and first subway system (Tremont Street Subway, 1897).[18]
The Boston area's many colleges and universities make it an international center of higher education,[19] including law, medicine, engineering, and business, and the city is considered to be a world leader in innovation and entrepreneurship, with nearly 2,000 startups.[20][21][22] Boston's economic base also includes finance,[23] professional and business services, biotechnology, information technology, and government activities.[24] Households in the city claim the highest average rate of philanthropy in the United States;[25] businesses and institutions rank among the top in the country for environmental sustainability and investment.[26] The city has one of the highest costs of living in the United States[27][28] as it has undergone gentrification,[29] though it remains high on world livability rankings.[30]
Contents
1 History
1.1 Colonial
1.2 Revolution and the Siege of Boston
1.3 Post-revolution and the War of 1812
1.4 19th century
1.5 20th century
1.6 21st century
2 Geography
2.1 Cityscapes
2.2 Neighborhoods
2.3 Climate
3 Demographics
3.1 Ancestry
3.2 Demographic breakdown by ZIP Code
3.2.1 Income
3.3 Religion
4 Economy
5 Education
5.1 Primary and secondary education
5.2 Higher education
6 Public safety
7 Culture
8 Environment
8.1 Pollution control
8.2 Water purity and availability
9 Sports
10 Parks and recreation
11 Government and politics
12 Media
12.1 Newspapers
12.2 Radio and television
12.3 Film
13 Healthcare
14 Infrastructure
14.1 Transportation
15 Twin towns and sister cities
16 See also
17 Notes
18 References
18.1 Sources
19 Further reading
20 External links
History
Colonial
Boston's early European settlers had first called the area Trimountaine (after its "three mountains," only traces of which remain today) but later renamed it Boston after Boston, Lincolnshire, England, the origin of several prominent colonists. The renaming on September 7, 1630, (Old Style)[31][b] was by Puritan colonists from England[13][32] who had moved over from Charlestown earlier that year in quest of fresh water. Their settlement was initially limited to the Shawmut Peninsula, at that time surrounded by the Massachusetts Bay and Charles River and connected to the mainland by a narrow isthmus. The peninsula is thought to have been inhabited as early as 5000 BC.[33]
In 1629, the Massachusetts Bay Colony's first governor John Winthrop led the signing of the Cambridge Agreement, a key founding document of the city. Puritan ethics and their focus on education influenced its early history;[34] America's first public school was founded in Boston in 1635.[17] Over the next 130 years, the city participated in four French and Indian Wars, until the British defeated the French and their Indian allies in North America.
Boston was the largest town in British America until Philadelphia grew larger in the mid-18th century.[35] Boston's oceanfront location made it a lively port, and the city primarily engaged in shipping and fishing during its colonial days. However, Boston stagnated in the decades prior to the Revolution. By the mid-18th century, New York City and Philadelphia surpassed Boston in wealth. Boston encountered financial difficulties even as other cities in New England grew rapidly.[36][37]
Revolution and the Siege of Boston

A south east view of the great town of Boston in New England in America (c. 1730)

In 1773, a group of Boston rebels threw a shipment of tea by the British East India Company into Boston Harbor as a response to the Tea Act, in an event known as the Boston Tea Party
.mw-parser-output .quotebox{background-color:#F9F9F9;border:1px solid #aaa;box-sizing:border-box;padding:10px;font-size:88%}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft{margin:0.5em 1.4em 0.8em 0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright{margin:0.5em 0 0.8em 1.4em}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.centered{margin:0.5em auto 0.8em auto}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft p,.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright p{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-title{background-color:#F9F9F9;text-align:center;font-size:larger;font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:before{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" “ ";vertical-align:-45%;line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:after{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" ” ";line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .left-aligned{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .right-aligned{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .center-aligned{text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .quotebox cite{display:block;font-style:normal}@media screen and (max-width:360px){.mw-parser-output .quotebox{min-width:100%;margin:0 0 0.8em!important;float:none!important}}
William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, in a letter to William Legge, 2nd Earl of Dartmouth about the British army's decision to leave Boston, dated March 21, 1776.[38]
Many of the crucial events of the American Revolution[39] occurred in or near Boston. Boston's penchant for mob action along with the colonists' growing distrust in Britain fostered a revolutionary spirit in the city.[36] When the British government passed the Stamp Act in 1765, a Boston mob ravaged the homes of Andrew Oliver, the official tasked with enforcing the Act, and Thomas Hutchinson, then the Lieutenant Governor of Massachusetts.[36][40] The British sent two regiments to Boston in 1768 in an attempt to quell the angry colonists. This did not sit well with the colonists. In 1770, during the Boston Massacre, the army killed several people in response to a mob in Boston. The colonists compelled the British to withdraw their troops. The event was widely publicized and fueled a revolutionary movement in America.[37]
In 1773, Britain passed the Tea Act. Many of the colonists saw the act as an attempt to force them to accept the taxes established by the Townshend Acts. The act prompted the Boston Tea Party, where a group of rebels threw an entire shipment of tea sent by the British East India Company into Boston Harbor. The Boston Tea Party was a key event leading up to the revolution, as the British government responded furiously with the Intolerable Acts, demanding compensation for the lost tea from the rebels.[36] This angered the colonists further and led to the American Revolutionary War. The war began in the area surrounding Boston with the Battles of Lexington and Concord.[36][41]
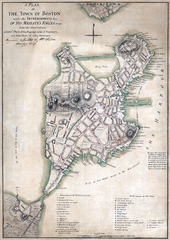
Map showing a British tactical evaluation of Boston in 1775
Boston itself was besieged for almost a year during the Siege of Boston, which began on April 19, 1775. The New England militia impeded the movement of the British Army. William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, then the commander-in-chief of the British forces in North America, led the British army in the siege. On June 17, the British captured the Charlestown peninsula in Boston, during the Battle of Bunker Hill. The British army outnumbered the militia stationed there, but it was a Pyrrhic victory for the British because their army suffered devastating casualties. It was also a testament to the power and courage of the militia, as their stubborn defending made it difficult for the British to capture Charlestown without losing many troops.[42][43]
Several weeks later, George Washington took over the militia after the Continental Congress established the Continental Army to unify the revolutionary effort. Both sides faced difficulties and supply shortages in the siege, and the fighting was limited to small-scale raids and skirmishes. On March 4, 1776, Washington commanded his army to fortify Dorchester Heights, an area of Boston. The army placed cannons there to repel a British invasion against their stake in Boston. Washington was confident that the army would be able to resist a small-scale invasion with their fortifications. Howe planned an invasion into Boston, but bad weather delayed their advance. Howe decided to withdraw, because the storm gave Washington's army more time to improve their fortifications. British troops evacuated Boston on March 17, which solidified the revolutionaries' control of the city.[41][42]
Post-revolution and the War of 1812

State Street, 1801
After the Revolution, Boston's long seafaring tradition helped make it one of the world's wealthiest international ports, with the slave trade,[44] rum, fish, salt, and tobacco being particularly important.[45] Boston's harbor activity was significantly curtailed by the Embargo Act of 1807 (adopted during the Napoleonic Wars) and the War of 1812. Foreign trade returned after these hostilities, but Boston's merchants had found alternatives for their capital investments in the interim. Manufacturing became an important component of the city's economy, and the city's industrial manufacturing overtook international trade in economic importance by the mid-19th century. Boston remained one of the nation's largest manufacturing centers until the early 20th century, and was known for its garment production and leather-goods industries.[46] A network of small rivers bordering the city and connecting it to the surrounding region facilitated shipment of goods and led to a proliferation of mills and factories. Later, a dense network of railroads furthered the region's industry and commerce.[47]
Cutting down Beacon Hill in 1811; a view from the north toward the Massachusetts State House[48]
During this period, Boston flourished culturally, as well, admired for its rarefied literary life and generous artistic patronage,[49][50] with members of old Boston families—eventually dubbed Boston Brahmins—coming to be regarded as the nation's social and cultural elites.[51]
Boston was an early port of the Atlantic triangular slave trade in the New England colonies, but was soon overtaken by Salem, Massachusetts and Newport, Rhode Island.[52] Boston eventually became a center of the abolitionist movement.[53] The city reacted strongly to the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850,[54] contributing to President Franklin Pierce's attempt to make an example of Boston after the Anthony Burns Fugitive Slave Case.[55][56]
In 1822,[14] the citizens of Boston voted to change the official name from the "Town of Boston" to the "City of Boston", and on March 4, 1822, the people of Boston accepted the charter incorporating the City.[57] At the time Boston was chartered as a city, the population was about 46,226, while the area of the city was only 4.7 square miles (12 km2).[57]
19th century
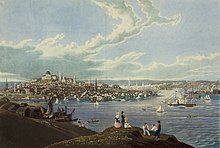
View of Boston from Dorchester Heights, 1841

Tremont Street, 1843
In the 1820s, Boston's population grew rapidly, and the city's ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European immigrants. Irish immigrants dominated the first wave of newcomers during this period, especially following the Irish Potato Famine; by 1850, about 35,000 Irish lived in Boston.[58] In the latter half of the 19th century, the city saw increasing numbers of Irish, Germans, Lebanese, Syrians,[59]French Canadians, and Russian and Polish Jews settling in the city. By the end of the 19th century, Boston's core neighborhoods had become enclaves of ethnically distinct immigrants. Italians inhabited the North End,[60] Irish dominated South Boston and Charlestown, and Russian Jews lived in the West End. Irish and Italian immigrants brought with them Roman Catholicism. Currently, Catholics make up Boston's largest religious community,[61] and the Irish have played a major role in Boston politics since the early 20th century; prominent figures include the Kennedys, Tip O'Neill, and John F. Fitzgerald.[62]
Between 1631 and 1890, the city tripled its area through land reclamation by filling in marshes, mud flats, and gaps between wharves along the waterfront.[63] The largest reclamation efforts took place during the 19th century; beginning in 1807, the crown of Beacon Hill was used to fill in a 50-acre (20 ha) mill pond that later became the Haymarket Square area. The present-day State House sits atop this lowered Beacon Hill. Reclamation projects in the middle of the century created significant parts of the South End, the West End, the Financial District, and Chinatown.

The Old City Hall was home to the Boston city council from 1865 to 1969.

Haymarket Square, 1909
After the Great Boston fire of 1872, workers used building rubble as landfill along the downtown waterfront. During the mid-to-late 19th century, workers filled almost 600 acres (2.4 km2) of brackish Charles River marshlands west of Boston Common with gravel brought by rail from the hills of Needham Heights. The city annexed the adjacent towns of South Boston (1804), East Boston (1836), Roxbury (1868), Dorchester (including present-day Mattapan and a portion of South Boston) (1870), Brighton (including present-day Allston) (1874), West Roxbury (including present-day Jamaica Plain and Roslindale) (1874), Charlestown (1874), and Hyde Park (1912).[64][65] Other proposals were unsuccessful for the annexation of Brookline, Cambridge,[66] and Chelsea.[67][68]
20th century
The city went into decline by the early to mid-20th century, as factories became old and obsolete and businesses moved out of the region for cheaper labor elsewhere.[69] Boston responded by initiating various urban renewal projects, under the direction of the Boston Redevelopment Authority (BRA) established in 1957. In 1958, BRA initiated a project to improve the historic West End neighborhood. Extensive demolition was met with strong public opposition.[70]
The BRA subsequently re-evaluated its approach to urban renewal in its future projects, including the construction of the Government Center. In 1965, the Columbia Point Health Center opened in the Dorchester neighborhood, the first Community Health Center in the United States. It mostly served the massive Columbia Point public housing complex adjoining it, which was built in 1953. The health center is still in operation and was rededicated in 1990 as the Geiger-Gibson Community Health Center.[71] The Columbia Point complex itself was redeveloped and revitalized from 1984 to 1990 into a mixed-income residential development called Harbor Point Apartments.[72]
By the 1970s, the city's economy had recovered after 30 years of economic downturn. A large number of high-rises were constructed in the Financial District and in Boston's Back Bay during this period.[73] This boom continued into the mid-1980s and resumed after a few pauses. Hospitals such as Massachusetts General Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and Brigham and Women's Hospital lead the nation in medical innovation and patient care. Schools such as Boston College, Boston University, the Harvard Medical School, Tufts University School of Medicine, Northeastern University, Massachusetts College of Art and Design, Wentworth Institute of Technology, Berklee College of Music, and Boston Conservatory attract students to the area. Nevertheless, the city experienced conflict starting in 1974 over desegregation busing, which resulted in unrest and violence around public schools throughout the mid-1970s.[74]
21st century

Back Bay neighborhood
Boston is an intellectual, technological, and political center but has lost some important regional institutions,[75] including the loss to mergers and acquisitions of local financial institutions such as FleetBoston Financial, which was acquired by Charlotte-based Bank of America in 2004.[76] Boston-based department stores Jordan Marsh and Filene's have both merged into the Cincinnati–based Macy's.[77]
The 1993 acquisition of The Boston Globe by The New York Times[78] was reversed in 2013 when it was re-sold to Boston businessman John W. Henry. In 2016, it was announced that General Electric would be moving its corporate headquarters from Connecticut to the Innovation District in South Boston, joining many other companies in this rapidly developing neighborhood.
Boston has experienced gentrification in the latter half of the 20th century,[79] with housing prices increasing sharply since the 1990s.[28] Living expenses have risen; Boston has one of the highest costs of living in the United States[80] and was ranked the 129th-most expensive major city in the world in a 2011 survey of 214 cities.[81] Despite cost-of-living issues, Boston ranks high on livability ratings, ranking 36th worldwide in quality of living in 2011 in a survey of 221 major cities.[82]
On April 15, 2013, two Chechen Islamist brothers detonated a pair of bombs near the finish line of the Boston Marathon, killing three people and injuring roughly 264.[83]
In 2016, Boston briefly shouldered a bid as the US applicant for the 2024 Summer Olympics. The bid was supported by the mayor and a coalition of business leaders and local philanthropists, but was eventually dropped due to public opposition.[84] The USOC then selected Los Angeles to be the American candidate with Los Angeles ultimately securing the right to host the 2028 Summer Olympics.
Geography

Boston as seen from the International Space Station (ISS)
Boston has an area of 89.63 square miles (232.1 km2)—48.4 square miles (125.4 km2) (54%) of land and 41.2 square miles (106.7 km2) (46%) of water. The city's official elevation, as measured at Logan International Airport, is 19 ft (5.8 m) above sea level.[85] The highest point in Boston is Bellevue Hill at 330 feet (100 m) above sea level, and the lowest point is at sea level.[86] Situated onshore of the Atlantic Ocean, Boston is the only state capital in the contiguous United States with an oceanic shoreline.[87]
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
The geographical center of Boston is in Roxbury. Due north of the center we find the South End. This is not to be confused with South Boston which lies directly east from the South End. North of South Boston is East Boston and southwest of East Boston is the North End.
— Author, Unknown – A common local colloquialism
Boston is surrounded by the "Greater Boston" region and is contiguously bordered by the cities and towns of Winthrop, Revere, Chelsea, Everett, Somerville, Cambridge, Watertown, Newton, Brookline, Needham, Dedham, Canton, Milton, and Quincy. The Charles River separates Boston from Watertown and the majority of Cambridge, and the mass of Boston from its own Charlestown neighborhood. To the east lie Boston Harbor and the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area (which includes part of the city's territory, specifically Calf Island, Gallops Island, Great Brewster Island, Green Island, Little Brewster Island, Little Calf Island, Long Island, Lovells Island, Middle Brewster Island, Nixes Mate, Outer Brewster Island, Rainsford Island, Shag Rocks, Spectacle Island, The Graves, and Thompson Island). The Neponset River forms the boundary between Boston's southern neighborhoods and the city of Quincy and the town of Milton. The Mystic River separates Charlestown from Chelsea and Everett, and Chelsea Creek and Boston Harbor separate East Boston from Boston proper.[88]
Cityscapes
Neighborhoods

200 Clarendon Street is the tallest building in Boston, with a roof height of 790 feet (240 m).
Boston is sometimes called a "city of neighborhoods" because of the profusion of diverse subsections; the city government's Office of Neighborhood Services has officially designated 23 neighborhoods.[89] More than two-thirds of inner Boston's modern land area did not exist when the city was founded. Instead, it was created via the gradual filling in of the surrounding tidal areas over the centuries,[63] with earth from leveling or lowering Boston's three original hills (the "Trimountain", after which Tremont Street is named) and with gravel brought by train from Needham to fill the Back Bay.[15]
Downtown and its immediate surroundings consist largely of low-rise masonry buildings (often Federal style and Greek Revival) interspersed with modern highrises, in the Financial District, Government Center, and South Boston.[90] Back Bay includes many prominent landmarks, such as the Boston Public Library, Christian Science Center, Copley Square, Newbury Street, and New England's two tallest buildings: the John Hancock Tower and the Prudential Center.[91]
Near the John Hancock Tower is the old John Hancock Building with its prominent illuminated beacon, the color of which forecasts the weather.[92] Smaller commercial areas are interspersed among areas of single-family homes and wooden/brick multi-family row houses. The South End Historic District is the largest surviving contiguous Victorian-era neighborhood in the US.[93] The geography of downtown and South Boston was particularly affected by the Central Artery/Tunnel Project (known unofficially as the "Big Dig") which removed the unsightly elevated Central Artery and incorporated new green spaces and open areas.[94]
Climate

Boston's skyline in the background, with fall foliage in the foreground
| Boston, MA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Under the Köppen climate classification, Boston has a hot summer humid continental climate (Köppen Dfa).[95] Summers are typically warm and humid, while winters are cold and stormy, with occasional periods of heavy snow. Spring and fall are usually cool to mild, with varying conditions dependent on wind direction and jet stream positioning. Prevailing wind patterns that blow offshore minimize the influence of the Atlantic Ocean. However, in winter areas near the immediate coast will often see more rain than snow as warm air is drawn off the Atlantic at times.[96] The city lies at the transition between USDA plant hardiness zones 6b (most of the city) and 7a (Downtown, South Boston, and East Boston neighborhoods).[97]
The hottest month is July, with a mean temperature of 73.4 °F (23.0 °C). The coldest month is January, with a mean of 29.0 °F (−1.7 °C). Periods exceeding 90 °F (32 °C) in summer and below freezing in winter are not uncommon but rarely extended, with about 13 and 25 days per year seeing each, respectively.[98] The most recent sub-0 °F (−18 °C) reading occurred on January 7, 2018, when the temperature dipped down to −2 °F (−19 °C).[98] In addition, several decades may pass between 100 °F (38 °C) readings, with the most recent such occurrence on July 22, 2011, when the temperature reached 103 °F (39 °C).[98] The city's average window for freezing temperatures is November 9 through April 5.[98][c] Official temperature records have ranged from −18 °F (−28 °C) on February 9, 1934, up to 104 °F (40 °C) on July 4, 1911. The record cold daily maximum is 2 °F (−17 °C) on December 30, 1917 while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum is 83 °F (28 °C) on August 2, 1975.[99]

A graph of cumulative winter snowfall at Logan International Airport from 1938–2015. The four winters with the greatest amount of snowfall are highlighted. The snowfall data, which was collected by NOAA, is from the weather station at the airport.
Boston's coastal location on the North Atlantic moderates its temperature but makes the city very prone to Nor'easter weather systems that can produce much snow and rain.[96] The city averages 43.8 inches (1,110 mm) of precipitation a year, with 43.8 inches (111 cm) of snowfall per season.[98] Snowfall increases dramatically as one goes inland away from the city (especially north and west of the city)—away from the moderating influence of the ocean.[100] Most snowfall occurs from mid-November through early April, and snow is rare in May and October.[101][102] There is also high year-to-year variability in snowfall; for instance, the winter of 2011–12 saw only 9.3 in (23.6 cm) of accumulating snow, but the previous winter, the corresponding figure was 81.0 in (2.06 m).[98][d]
Fog is fairly common, particularly in spring and early summer. Due to its location along the North Atlantic, the city often receives sea breezes, especially in the late spring, when water temperatures are still quite cold and temperatures at the coast can be more than 20 °F (11 °C) colder than a few miles inland, sometimes dropping by that amount near midday.[103][104]
Thunderstorms occur from May to September, that are occasionally severe with large hail, damaging winds and heavy downpours.[96] Although downtown Boston has never been struck by a violent tornado, the city itself has experienced many tornado warnings. Damaging storms are more common to areas north, west, and northwest of the city.[105] Boston has a relatively sunny climate for a coastal city at its latitude, averaging over 2,600 hours of sunshine per annum.
| Climate data for Boston (Logan Airport), 1981−2010 normals,[e] extremes 1872−present[f] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 72 (22) | 73 (23) | 89 (32) | 94 (34) | 97 (36) | 100 (38) | 104 (40) | 102 (39) | 102 (39) | 90 (32) | 83 (28) | 76 (24) | 104 (40) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 56.4 (13.6) | 57.7 (14.3) | 67.6 (19.8) | 80.7 (27.1) | 87.3 (30.7) | 92.1 (33.4) | 94.9 (34.9) | 93.3 (34.1) | 87.9 (31.1) | 79.1 (26.2) | 70.5 (21.4) | 61.3 (16.3) | 96.2 (35.7) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 35.8 (2.1) | 38.7 (3.7) | 45.4 (7.4) | 55.6 (13.1) | 66.0 (18.9) | 75.9 (24.4) | 81.4 (27.4) | 79.6 (26.4) | 72.4 (22.4) | 61.4 (16.3) | 51.5 (10.8) | 41.2 (5.1) | 58.8 (14.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 29.0 (−1.7) | 31.7 (−0.2) | 38.3 (3.5) | 48.1 (8.9) | 57.9 (14.4) | 67.7 (19.8) | 73.4 (23) | 72.1 (22.3) | 64.9 (18.3) | 54.0 (12.2) | 44.7 (7.1) | 34.7 (1.5) | 51.5 (10.8) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 22.2 (−5.4) | 24.7 (−4.1) | 31.1 (−0.5) | 40.6 (4.8) | 49.9 (9.9) | 59.5 (15.3) | 65.4 (18.6) | 64.6 (18.1) | 57.4 (14.1) | 46.5 (8.1) | 38.0 (3.3) | 28.2 (−2.1) | 44.1 (6.7) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 4.1 (−15.5) | 8.5 (−13.1) | 14.7 (−9.6) | 30.7 (−0.7) | 40.8 (4.9) | 49.6 (9.8) | 57.3 (14.1) | 55.4 (13) | 45.8 (7.7) | 34.9 (1.6) | 24.2 (−4.3) | 11.1 (−11.6) | 2.3 (−16.5) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −13 (−25) | −18 (−28) | −8 (−22) | 11 (−12) | 31 (−1) | 41 (5) | 50 (10) | 46 (8) | 34 (1) | 25 (−4) | −2 (−19) | −17 (−27) | −18 (−28) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.36 (85.3) | 3.25 (82.6) | 4.32 (109.7) | 3.74 (95) | 3.49 (88.6) | 3.68 (93.5) | 3.43 (87.1) | 3.35 (85.1) | 3.44 (87.4) | 3.94 (100.1) | 3.99 (101.3) | 3.78 (96) | 43.77 (1,111.8) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 12.9 (32.8) | 10.9 (27.7) | 7.8 (19.8) | 1.9 (4.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | trace | 1.3 (3.3) | 9.0 (22.9) | 43.8 (111.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 11.3 | 9.8 | 11.6 | 11.2 | 12.0 | 10.9 | 9.6 | 9.4 | 8.6 | 9.4 | 10.6 | 11.6 | 126.0 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 6.7 | 5.3 | 4.2 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 4.6 | 22.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 62.3 | 62.0 | 63.1 | 63.0 | 66.7 | 68.5 | 68.4 | 70.8 | 71.8 | 68.5 | 67.5 | 65.4 | 66.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 163.4 | 168.4 | 213.7 | 227.2 | 267.3 | 286.5 | 300.9 | 277.3 | 237.1 | 206.3 | 143.2 | 142.3 | 2,633.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 56 | 57 | 58 | 57 | 59 | 63 | 65 | 64 | 63 | 60 | 49 | 50 | 59 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961−1990)[107][98][108] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
This section is in a list format that may be better presented using prose. (November 2018) |
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1722 | 10,567 | — |
| 1765 | 15,520 | +46.9% |
| 1790 | 18,320 | +18.0% |
| 1800 | 24,937 | +36.1% |
| 1810 | 33,787 | +35.5% |
| 1820 | 43,298 | +28.1% |
| 1830 | 61,392 | +41.8% |
| 1840 | 93,383 | +52.1% |
| 1850 | 136,881 | +46.6% |
| 1860 | 177,840 | +29.9% |
| 1870 | 250,526 | +40.9% |
| 1880 | 362,839 | +44.8% |
| 1890 | 448,477 | +23.6% |
| 1900 | 560,892 | +25.1% |
| 1910 | 670,585 | +19.6% |
| 1920 | 748,060 | +11.6% |
| 1930 | 781,188 | +4.4% |
| 1940 | 770,816 | −1.3% |
| 1950 | 801,444 | +4.0% |
| 1960 | 697,197 | −13.0% |
| 1970 | 641,071 | −8.1% |
| 1980 | 562,994 | −12.2% |
| 1990 | 574,283 | +2.0% |
| 2000 | 589,141 | +2.6% |
| 2010 | 617,594 | +4.8% |
| 2017 | 685,094 | +10.9% |
| * = population estimate. Source: United States Census records and Population Estimates Program data.[109][110][111][112][113][114][115][116][117][118][119][120] Source: U.S. Decennial Census[121] | ||

Per capita income in the Greater Boston area, by US Census block group, 2000. The dashed line shows the boundary of the City of Boston.

Map of racial distribution in Boston, 2010 U.S. Census. Each dot is 25 people: White, Black, Asian, Hispanic, or Other (yellow)
In 2016, Boston was estimated to have 673,184 residents (a density of 13,841 persons/sq mi, or 5,344/km2) living in 272,481 housing units[2]—a 9% population increase over 2010. The city is the third-most densely populated large U.S. city of over half a million residents. Some 1.2 million persons may be within Boston's boundaries during work hours, and as many as 2 million during special events. This fluctuation of people is caused by hundreds of thousands of suburban residents who travel to the city for work, education, health care, and special events.[122]
In the city, the population was spread out with 21.9% at age 19 and under, 14.3% from 20 to 24, 33.2% from 25 to 44, 20.4% from 45 to 64, and 10.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 30.8 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.9 males.[123] There were 252,699 households, of which 20.4% had children under the age of 18 living in them, 25.5% were married couples living together, 16.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 54.0% were non-families. 37.1% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.26 and the average family size was 3.08.[123] Boston has one of the largest LGBT populations in the United States.
The median household income in Boston was $51,739, while the median income for a family was $61,035. Full-time year-round male workers had a median income of $52,544 versus $46,540 for full-time year-round female workers. The per capita income for the city was $33,158. 21.4% of the population and 16.0% of families are below the poverty line. Of the total population, 28.8% of those under the age of 18 and 20.4% of those 65 and older were living below the poverty line.[124]
In 1950, Whites represented 94.7% of Boston's population.[125] From the 1950s to the end of the 20th century, the proportion of non-Hispanic whites in the city declined. In 2000, non-Hispanic whites made up 49.5% of the city's population, making the city majority minority for the first time. However, in the 21st century, the city has experienced significant gentrification, in which affluent whites have moved into formerly non-white areas. In 2006, the US Census Bureau estimated that non-Hispanic whites again formed a slight majority but as of 2010[update], in part due to the housing crash, as well as increased efforts to make more affordable housing more available, the non-white population has rebounded. This may also have to do with increased Latin American and Asian populations and more clarity surrounding US Census statistics, which indicate a non-Hispanic white population of 47 percent (some reports give slightly lower figures).[126][127][128]
| Race/ethnicity | 2015[129] | 1990[125] | 1970[125] | 1940[125] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
White (includes White Hispanics) | 62.1% | 62.8% | 81.8% | 96.7% |
| Black | 24.7% | 25.6% | 16.3% | 3.1% |
| Asian | 9.1% | 5.3% | 1.3% | 0.2% |
| Native American | 0.8% | 0.3% | 0.2% | – |
| Two or more races | 3.1% | – | – | – |
Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 22.1% | 10.8% | 2.8% [130] | 0.1% |
| Non-Hispanic whites | 46.2% | 59.0% | 79.5% [130] | 96.6% |
| Race | Percentage of Boston population | Percentage of Massachusetts population | Percentage of United States population | City-to-State Difference | City-to-USA Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 53.0% | 81.3% | 76.6% | –28.3% | –23.6% |
| White (Non-Hispanic) | 45.3% | 72.1% | 60.7% | –26.8% | –15.4% |
| Black | 25.4% | 8.8% | 13.4% | +16.6% | +12.0% |
| Hispanic | 19.0% | 11.9% | 18.1% | +7.1% | +0.9% |
| Asian | 9.3% | 6.9% | 5.8% | +2.4% | +3.5% |
Native Americans/Hawaiians | 0.4% | 0.6% | 1.5% | –0.2% | –1.1% |
| Two or more races | 4.9% | 2.4% | 2.7% | +2.5% | +2.2% |

Chinatown, with its paifang gate, is home to many Chinese and also Vietnamese restaurants.

U.S. Navy sailors march in Boston's annual St. Patrick's Day Parade. Irish Americans constitute the largest ethnicity in Boston.
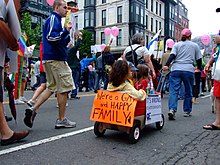
Boston gay pride march, held annually in June
People of Irish descent form the largest single ethnic group in the city, making up 15.8% of the population, followed by Italians, accounting for 8.3% of the population. People of West Indian and Caribbean ancestry are another sizable group, at 6.0%,[133] about half of whom are of Haitian ancestry. Over 27,000 Chinese Americans made their home in Boston city proper in 2013,[134] and the city hosts a growing Chinatown accommodating heavily traveled Chinese-owned bus lines to and from Chinatown, Manhattan in New York City. Some neighborhoods, such as Dorchester, have received an influx of people of Vietnamese ancestry in recent decades. Neighborhoods such as Jamaica Plain and Roslindale have experienced a growing number of Dominican Americans.[135] The city and greater area also has a growing immigrant population of South Asians, including the tenth-largest Indian population in the country.
The city, especially the East Boston neighborhood, has a significant Hispanic population. In 2010, Hispanics in Boston were mostly of Puerto Rican (30,506 or 4.9% of total city population), Dominican (25,648 or 4.2% of total city population), Salvadoran (10,850 or 1.8% of city population), Colombian (6,649 or 1.1% of total city population), Mexican (5,961 or 1.0% of total city population), and Guatemalan (4,451 or 0.7% of total city population) ethnic origin. Hispanics of all national origins totaled 107,917 in 2010. In Greater Boston, these numbers grew significantly, with Puerto Ricans numbering 175,000+, Dominicans 95,000+, Salvadorans 40,000+, Guatemalans 31,000+, Mexicans 25,000+, and Colombians numbering 22,000+.[136]
Ancestry
According to the 2012-2016 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates, the largest ancestry groups in Boston, Massachusetts are:[137][138]
| Ancestry | Percentage of Boston population | Percentage of Massachusetts population | Percentage of United States population | City-to-State Difference | City-to-USA Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Irish | 14.06% | 21.16% | 10.39% | –7.10% | +3.67% |
Italian | 8.13% | 13.19% | 5.39% | –5.05% | +2.74% |
West Indian | 6.92% | 1.96% | 0.90% | +4.97% | +6.02% |
Puerto Rican | 5.27% | 4.52% | 1.66% | +0.75% | +3.61% |
Chinese | 4.57% | 2.28% | 1.24% | +2.29% | +3.33% |
German | 4.57% | 6.00% | 14.40% | –1.43% | –9.83% |
English | 4.54% | 9.77% | 7.67% | –5.23% | –3.13% |
American | 4.13% | 4.26% | 6.89% | –0.13% | –2.76% |
Sub-Saharan African | 4.09% | 2.00% | 1.01% | +2.09% | +3.08% |
Haitian | 3.58% | 1.15% | 0.31% | +2.43% | +3.27% |
Polish | 2.48% | 4.67% | 2.93% | –2.19% | –0.45% |
Cape Verdean | 2.21% | 0.97% | 0.03% | +1.24% | +2.18% |
French | 1.93% | 6.82% | 2.56% | –4.89% | –0.63% |
Vietnamese | 1.76% | 0.69% | 0.54% | +1.07% | +1.22% |
Jamaican | 1.70% | 0.44% | 0.34% | +1.26% | +1.36% |
Russian | 1.62% | 1.65% | 0.88% | –0.03% | +0.74% |
Asian Indian | 1.31% | 1.39% | 1.09% | –0.08% | +0.22% |
Scottish | 1.30% | 2.28% | 1.71% | –0.98% | –0.41% |
French Canadian | 1.19% | 3.91% | 0.65% | –2.71% | +0.54% |
Mexican | 1.12% | 0.67% | 11.96% | +0.45% | –10.84% |
Arab | 1.10% | 1.10% | 0.59% | +0.00% | +0.50% |
Demographic breakdown by ZIP Code
Income
Data is from the 2008–2012 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates.[139][140][141]
| Rank | ZIP code (ZCTA) | Per capita income | Median household income | Median family income | Population | Number of households |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 02110 (Financial District) | $152,007 | $123,795 | $196,518 | 1,486 | 981 |
| 2 | 02199 (Prudential Center) | $151,060 | $107,159 | $146,786 | 1,290 | 823 |
| 3 | 02210 (Fort Point) | $93,078 | $111,061 | $223,411 | 1,905 | 1,088 |
| 4 | 02109 (North End) | $88,921 | $128,022 | $162,045 | 4,277 | 2,190 |
| 5 | 02116 (Back Bay/Bay Village) | $81,458 | $87,630 | $134,875 | 21,318 | 10,938 |
| 6 | 02108 (Beacon Hill/Financial District) | $78,569 | $95,753 | $153,618 | 4,155 | 2,337 |
| 7 | 02114 (Beacon Hill/West End) | $65,865 | $79,734 | $169,107 | 11,933 | 6,752 |
| 8 | 02111 (Chinatown/Financial District/Leather District) | $56,716 | $44,758 | $88,333 | 7,616 | 3,390 |
| 9 | 02129 (Charlestown) | $56,267 | $89,105 | $98,445 | 17,052 | 8,083 |
| 10 | 02467 (Chestnut Hill) | $53,382 | $113,952 | $148,396 | 22,796 | 6,351 |
| 11 | 02113 (North End) | $52,905 | $64,413 | $112,589 | 7,276 | 4,329 |
| 12 | 02132 (West Roxbury) | $44,306 | $82,421 | $110,219 | 27,163 | 11,013 |
| 13 | 02118 (South End) | $43,887 | $50,000 | $49,090 | 26,779 | 12,512 |
| 14 | 02130 (Jamaica Plain) | $42,916 | $74,198 | $95,426 | 36,866 | 15,306 |
| 15 | 02127 (South Boston) | $42,854 | $67,012 | $68,110 | 32,547 | 14,994 |
Massachusetts | $35,485 | $66,658 | $84,380 | 6,560,595 | 2,525,694 | |
Boston | $33,589 | $53,136 | $63,230 | 619,662 | 248,704 | |
Suffolk County | $32,429 | $52,700 | $61,796 | 724,502 | 287,442 | |
| 16 | 02135 (Brighton) | $31,773 | $50,291 | $62,602 | 38,839 | 18,336 |
| 17 | 02131 (Roslindale) | $29,486 | $61,099 | $70,598 | 30,370 | 11,282 |
United States | $28,051 | $53,046 | $64,585 | 309,138,711 | 115,226,802 | |
| 18 | 02136 (Hyde Park) | $28,009 | $57,080 | $74,734 | 29,219 | 10,650 |
| 19 | 02134 (Allston) | $25,319 | $37,638 | $49,355 | 20,478 | 8,916 |
| 20 | 02128 (East Boston) | $23,450 | $49,549 | $49,470 | 41,680 | 14,965 |
| 21 | 02122 (Dorchester-Fields Corner) | $23,432 | $51,798 | $50,246 | 25,437 | 8,216 |
| 22 | 02124 (Dorchester-Codman Square-Ashmont) | $23,115 | $48,329 | $55,031 | 49,867 | 17,275 |
| 23 | 02125 (Dorchester-Uphams Corner-Savin Hill) | $22,158 | $42,298 | $44,397 | 31,996 | 11,481 |
| 24 | 02163 (Allston-Harvard Business School) | $21,915 | $43,889 | $91,190 | 1,842 | 562 |
| 25 | 02115 (Back Bay/Fenway–Kenmore) | $21,654 | $23,677 | $50,303 | 29,178 | 9,958 |
| 26 | 02126 (Mattapan) | $20,649 | $43,532 | $52,774 | 27,335 | 9,510 |
| 27 | 02215 (Fenway-Kenmore) | $19,082 | $30,823 | $72,583 | 23,719 | 7,995 |
| 28 | 02119 (Roxbury) | $18,998 | $27,051 | $35,311 | 24,237 | 9,769 |
| 29 | 02121 (Dorchester-Mount Bowdoin) | $18,226 | $30,419 | $35,439 | 26,801 | 9,739 |
| 30 | 02120 (Mission Hill) | $17,390 | $32,367 | $29,583 | 13,217 | 4,509 |
Religion

Old South Church, a United Church of Christ congregation first organized in 1669
According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, 57% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christians, with 25% attending a variety Protestant churches and 29% professing Roman Catholic beliefs;[142][143] 33% claim no religious affiliation, while the remaining 10% are made up of adherents of Judaism, Buddhism, Islam, Hinduism and other faiths.
As of 2010[update] the Catholic Church had the highest number of adherents as a single denomination in the Boston-Cambridge-Newton Metro area, with more than two million members and 339 churches, followed by the Episcopal Church with 58,000 adherents in 160 churches. The United Church of Christ had 55,000 members and 213 churches.[144] The UCC is the successor of the city's Puritan religious traditions. Old South Church in Boston is one of the oldest congregations in the United States. It was organized in 1669 by dissenters from the First Church in Boston (1630). Past members include Samuel Adams, William Dawes, Benjamin Franklin, Samuel Sewall, and Phillis Wheatley. In 1773, Adams gave the signals from the Old South Meeting House that started the Boston Tea Party.
The city has a Jewish population with an estimated 248,000 Jews within the Boston metro area.[145] More than half of Jewish households in the Greater Boston area reside in the city itself, Brookline, Newton, Cambridge, Somerville, or adjacent towns.[145]
Economy
Top publicly traded Boston companies for 2018 (ranked by revenues) with City and U.S. ranks Source: Fortune 500[146] | |||||||
| Bos. | Corporation | US | Revenue (in millions) | ||||
| 1 | General Electric | 18 | $122,274 | ||||
| 2 | Liberty Mutual | 68 | $42,687 | ||||
| 3 | State Street | 259 | $11,774 | ||||
| 4 | American Tower | 419 | $6,663.9 | ||||
Top City Employers Source: MA Executive Office of Labor and Workforce Development[147] | |||||||
| Rank | Company/Organization | ||||||
| 1 | Brigham and Women's Hospital | ||||||
| 2 | Massachusetts General Hospital | ||||||
| 3 | Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center | ||||||
| 4 | Boston Children's Hospital | ||||||
| 5 | Boston Medical Center | ||||||
| 6 | BU School of Medicine | ||||||
| 7 | Boston University | ||||||
| 8 | Floating Hospital for Children | ||||||
| 9 | John Hancock Financial | ||||||
| 10 | Liberty Mutual | ||||||
Distribution of Greater Boston NECTA Labor Force (2016)[148]
Nat'l resources & mining (0%)
Construction (5%)
Manufacturing (8%)
Trade, transportation & utilities (15%)
Information (3%)
Finance & real estate (8%)
Professional & business services (15%)
Educational & health services (28%)
Leisure & hospitality (9%)
Other services (4%)
Government (4%)
A global city, Boston is placed among the top 30 most economically powerful cities in the world.[149] Encompassing $363 billion, the Greater Boston metropolitan area has the sixth-largest economy in the country and 12th-largest in the world.[150]
Boston's colleges and universities exert a significant impact on the regional economy. Boston attracts more than 350,000 college students from around the world, who contribute more than US$4.8 billion annually to the city's economy.[151][152] The area's schools are major employers and attract industries to the city and surrounding region. The city is home to a number of technology companies and is a hub for biotechnology, with the Milken Institute rating Boston as the top life sciences cluster in the country.[153] Boston receives the highest absolute amount of annual funding from the National Institutes of Health of all cities in the United States.[154]
The city is considered highly innovative for a variety of reasons, including the presence of academia, access to venture capital, and the presence of many high-tech companies.[21][155] The Route 128 corridor and Greater Boston continue to be a major center for venture capital investment,[156] and high technology remains an important sector.
Tourism also composes a large part of Boston's economy, with 21.2 million domestic and international visitors spending $8.3 billion in 2011.[157] Excluding visitors from Canada and Mexico, over 1.4 million international tourists visited Boston in 2014, with those from China and the United Kingdom leading the list.[158] Boston's status as a state capital as well as the regional home of federal agencies has rendered law and government to be another major component of the city's economy.[46][159] The city is a major seaport along the East Coast of the United States and the oldest continuously operated industrial and fishing port in the Western Hemisphere.[160]
The financial services industry is important to Boston, especially involving mutual funds and insurance.[46] In the 2017 Global Financial Centres Index, Boston was ranked as having the ninth-most competitive financial center in the world and the fourth-most competitive in the United States.[161] Boston-based Fidelity Investments helped popularize the mutual fund in the 1980s and has made Boston one of the top financial centers in the United States.[162][163] The city is home to the headquarters of Santander Bank, and Boston is a center for venture capital firms. State Street Corporation, which specializes in asset management and custody services, is based in the city. Boston is a printing and publishing center[164]—Houghton Mifflin Harcourt is headquartered within the city, along with Bedford-St. Martin's Press and Beacon Press. Pearson PLC publishing units also employ several hundred people in Boston. The city is home to three major convention centers—the Hynes Convention Center in the Back Bay, and the Seaport World Trade Center and Boston Convention and Exhibition Center on the South Boston waterfront.[165] The General Electric Corporation announced in January 2016 its decision to move the company's global headquarters to the Seaport District in Boston, from Fairfield, Connecticut, citing factors including Boston's preeminence in the realm of higher education.[166] Boston is home to the headquarters of several major athletic and footwear companies including Converse, New Balance, and Reebok. Rockport, Puma and Wolverine World Wide, Inc. headquarters or regional offices[167] are located just outside the city.[168]
Education
Primary and secondary education

Boston Latin School was established in 1635 and is the oldest public high school in the US.
The Boston Public Schools enroll 57,000 students attending 145 schools, including the renowned Boston Latin Academy, John D. O'Bryant School of Math & Science, and Boston Latin School. The Boston Latin School was established in 1635 and is the oldest public high school in the US. Boston also operates the United States' second-oldest public high school and its oldest public elementary school.[17] The system's students are 40% Hispanic or Latino, 35% Black or African American, 13% White, and 9% Asian.[169] There are private, parochial, and charter schools as well, and approximately 3,300 minority students attend participating suburban schools through the Metropolitan Educational Opportunity Council.[170]
Higher education

Map of Boston-area universities

Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is often cited as among the world's top universities.

Harvard Business School, one of the country's top business schools
Some of the most renowned and highly ranked universities in the world are located near Boston.[171][172] Three universities with a major presence in the city, Harvard, MIT, and Tufts, are located just outside of Boston in the cities of Cambridge and Somerville, known as the Brainpower Triangle.[173] Harvard is the nation's oldest institute of higher education and is centered across the Charles River in Cambridge, though the majority of its land holdings and a substantial amount of its educational activities are in Boston. Its business, medical, dental, and public health schools are located in Boston's Allston and Longwood neighborhoods, and Harvard has plans for additional expansion into Allston.[174]
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) originated in Boston and was long known as "Boston Tech"; it moved across the river to Cambridge in 1916.[175]Tufts University's main campus is north of the city in Somerville and Medford, though it locates its medical and dental schools in Boston's Chinatown at Tufts Medical Center, a 451-bed academic medical institution that is home to both a full-service hospital for adults and the Floating Hospital for Children.[176]
Four members of the Association of American Universities are in Greater Boston (more than any other metropolitan area): Harvard University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Boston University, and Brandeis University.[177] Furthermore, Greater Boston contains seven Highest Research Activity (R1) Universities as per the Carnegie Classification. This includes, in addition to the aforementioned four, Boston College, Northeastern University, and Tufts University. This is, by a large margin, the highest concentration of such institutions in a single metropolitan area.
Hospitals, universities, and research institutions in Greater Boston received more than $1.77 billion in National Institutes of Health grants in 2013, more money than any other American metropolitan area.[178]
Greater Boston has more than 100 colleges and universities, with 250,000 students enrolled in Boston and Cambridge alone.[179] The city's largest private universities include Boston University (also the city's fourth-largest employer),[180] with its main campus along Commonwealth Avenue and a medical campus in the South End, Northeastern University in the Fenway area,[181]Suffolk University near Beacon Hill, which includes law school and business school,[182] and Boston College, which straddles the Boston (Brighton)–Newton border.[183] Boston's only public university is the University of Massachusetts Boston on Columbia Point in Dorchester. Roxbury Community College and Bunker Hill Community College are the city's two public community colleges. Altogether, Boston's colleges and universities employ more than 42,600 people, accounting for nearly seven percent of the city's workforce.[184]
Smaller private colleges include Babson College, Bentley University, Boston Architectural College, Emmanuel College, Fisher College, MGH Institute of Health Professions, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Simmons College, Wellesley College, Wheelock College, Wentworth Institute of Technology, New England School of Law (originally established as America's first all female law school),[185] and Emerson College.[186]
Metropolitan Boston is home to several conservatories and art schools, including Lesley University College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art, the School of the Museum of Fine Arts, New England Institute of Art, New England School of Art and Design (Suffolk University), Longy School of Music of Bard College, and the New England Conservatory (the oldest independent conservatory in the United States).[187] Other conservatories include the Boston Conservatory and Berklee College of Music, which has made Boston an important city for jazz music.[188]
Public safety
A Boston Police cruiser on Beacon Street
Like many major American cities, Boston has seen a great reduction in violent crime since the early 1990s. Boston's low crime rate since the 1990s has been credited to the Boston Police Department's collaboration with neighborhood groups and church parishes to prevent youths from joining gangs, as well as involvement from the United States Attorney and District Attorney's offices. This helped lead in part to what has been touted as the "Boston Miracle". Murders in the city dropped from 152 in 1990 (for a murder rate of 26.5 per 100,000 people) to just 31—not one of them a juvenile—in 1999 (for a murder rate of 5.26 per 100,000).[189]
In 2008, there were 62 reported homicides.[190] Through December 30, 2016, major crime was down seven percent and there were 46 homicides compared to 40 in 2015.[191]
Culture

The Old State House, a museum on the Freedom Trail and the site of the Boston Massacre

In the nineteenth century, the Old Corner Bookstore became a gathering place for writers, including Emerson, Thoreau, and Margaret Fuller. Here James Russell Lowell printed the first editions of The Atlantic Monthly.
Boston shares many cultural roots with greater New England, including a dialect of the non-rhotic Eastern New England accent known as the Boston accent[192] and a regional cuisine with a large emphasis on seafood, salt, and dairy products.[193] Boston also has its own collection of neologisms known as Boston slang.[194]
In the early 1800s, William Tudor wrote that Boston was "'perhaps the most perfect and certainly the best-regulated democracy that ever existed. There is something so impossible in the immortal fame of Athens, that the very name makes everything modern shrink from comparison; but since the days of that glorious city I know of none that has approached so near in some points, distant as it may still be from that illustrious model.'[195] From this, Boston has been called the "Athens of America" (also a nickname of Philadelphia[196]) for its literary culture, earning a reputation as "the intellectual capital of the United States."[197]
In the nineteenth century, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry David Thoreau, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Margaret Fuller, James Russell Lowell, and Henry Wadsworth Longfellow wrote in Boston. Some consider the Old Corner Bookstore to be the "cradle of American literature," the place where these writers met and where The Atlantic Monthly was first published.[198] In 1852, the Boston Public Library was founded as the first free library in the United States.[197] Boston's literary culture continues today thanks to the city's many universities and the Boston Book Festival.
Music is afforded a high degree of civic support in Boston. The Boston Symphony Orchestra is one of the "Big Five," a group of the greatest American orchestras, and the classical music magazine Gramophone called it one of the "world's best" orchestras.[199]Symphony Hall (located west of Back Bay) is home to the Boston Symphony Orchestra and the related Boston Youth Symphony Orchestra, which is the largest youth orchestra in the nation, and to the Boston Pops Orchestra. The British newspaper The Guardian called Boston Symphony Hall "one of the top venues for classical music in the world," adding that "Symphony Hall in Boston was where science became an essential part of concert hall design."[200] Other concerts are held at the New England Conservatory's Jordan Hall. The Boston Ballet performs at the Boston Opera House. Other performing-arts organizations located in the city include the Boston Lyric Opera Company, Opera Boston, Boston Baroque (the first permanent Baroque orchestra in the US),[201] and the Handel and Haydn Society (one of the oldest choral companies in the United States).[202] The city is a center for contemporary classical music with a number of performing groups, several of which are associated with the city's conservatories and universities. These include the Boston Modern Orchestra Project and Boston Musica Viva.[201] Several theaters are located in or near the Theater District south of Boston Common, including the Cutler Majestic Theatre, Citi Performing Arts Center, the Colonial Theater, and the Orpheum Theatre.[203]

Symphony Hall, home of the Boston Symphony Orchestra

Museum of Fine Arts
There are several major annual events, such as First Night which occurs on New Year's Eve, the Boston Early Music Festival, the annual Boston Arts Festival at Christopher Columbus Waterfront Park, the annual Boston gay pride parade and festival held in June, and Italian summer feasts in the North End honoring Catholic saints.[204] The city is the site of several events during the Fourth of July period. They include the week-long Harborfest festivities[205] and a Boston Pops concert accompanied by fireworks on the banks of the Charles River.[206]
Several historic sites relating to the American Revolution period are preserved as part of the Boston National Historical Park because of the city's prominent role. Many are found along the Freedom Trail, which is marked by a red line of bricks embedded in the ground.
The city is also home to several art museums and galleries, including the Museum of Fine Arts and the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum.[207] The Institute of Contemporary Art is housed in a contemporary building designed by Diller Scofidio + Renfro in the Seaport District.[208] Boston's South End Art and Design District (SoWa) and Newbury St. are both art gallery destinations.[209][210] Columbia Point is the location of the University of Massachusetts Boston, the Edward M. Kennedy Institute for the United States Senate, the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum, and the Massachusetts Archives and Commonwealth Museum. The Boston Athenæum (one of the oldest independent libraries in the United States),[211]Boston Children's Museum, Bull & Finch Pub (whose building is known from the television show Cheers),[212]Museum of Science, and the New England Aquarium are within the city.
Boston has been a noted religious center from its earliest days. The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Boston serves nearly 300 parishes and is based in the Cathedral of the Holy Cross (1875) in the South End, while the Episcopal Diocese of Massachusetts serves just under 200 congregations, with the Cathedral Church of St. Paul (1819) as its episcopal seat. Unitarian Universalism has its headquarters on Beacon Hill. The Christian Scientists are headquartered in Back Bay at the Mother Church (1894). The oldest church in Boston is First Church in Boston, founded in 1630.[213]King's Chapel was the city's first Anglican church, founded in 1686 and converted to Unitarianism in 1785. Other churches include Christ Church (better known as Old North Church, 1723), the oldest church building in the city, Trinity Church (1733), Park Street Church (1809), Old South Church (1874), Jubilee Christian Church, and Basilica and Shrine of Our Lady of Perpetual Help on Mission Hill (1878).[214]
Environment
Pollution control
Air quality in Boston is generally very good. Between 2004–2013, there were only four days in which the air was unhealthy for the general public, according to the EPA.[215]
Some of the cleaner energy facilities in Boston include the Allston green district, with three ecologically compatible housing facilities.[216] Boston is also breaking ground on multiple green affordable housing facilities to help reduce the carbon impact of the city while simultaneously making these initiatives financially available to a greater population. Boston's climate plan is updated every three years and was most recently modified in 2013. This legislature includes the Building Energy Reporting and Disclosure Ordinance, which requires the city's larger buildings to disclose their yearly energy and water use statistics and to partake in an energy assessment every five years. These statistics are made public by the city, thereby increasing incentives for buildings to be more environmentally conscious.[217]
Mayor Thomas Menino introduced the Renew Boston Whole Building Incentive which reduces the cost of living in buildings that are deemed energy efficient. This gives people an opportunity to find housing in neighborhoods that support the environment. The ultimate goal of this initiative is to enlist 500 Bostonians to participate in a free, in-home energy assessment.[217]
Water purity and availability
Many older buildings in certain areas of Boston are supported by wooden piles driven into the area's fill; these piles remain sound if submerged in water, but are subject to dry rot if exposed to air for long periods.[218]
Ground water levels have been dropping in many areas of the city, due in part to an increase in the amount of rainwater discharged directly into sewers rather than absorbed by the ground. The Boston Groundwater Trust coordinates monitoring ground water levels throughout the city via a network of public and private monitoring wells.[219] However, Boston's drinking water supply from the Quabbin and Wachusett Reservoirs[220] is one of the very few in the country so pure as to satisfy the Federal Clean Water Act without filtration.[221]
Sports

Fenway Park is the oldest professional baseball stadium still in use.
Boston has teams in the four major North American professional sports leagues plus Major League Soccer, and has won 37 championships in these leagues, As of 2017[update]. It is one of five cities (along with Chicago, Los Angeles, New York and Philadelphia) to have won championships in all four major sports. It has been suggested[222][223][224] that Boston is the new "TitleTown, USA", as the city's professional sports teams have won eleven championships since 2001: Patriots (2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, and 2016), Red Sox (2004, 2007, 2013, and 2018), Celtics (2008), and Bruins (2011). This love of sports made Boston the United States Olympic Committee's choice to bid to hold the 2024 Summer Olympic Games, but the city cited financial concerns when it withdrew its bid on July 27, 2015.[225]
The Boston Red Sox, a founding member of the American League of Major League Baseball in 1901, play their home games at Fenway Park, near Kenmore Square in the city's Fenway section. Built in 1912, it is the oldest sports arena or stadium in active use in the United States among the four major professional American sports leagues, Major League Baseball, the National Football League, National Basketball Association, and the National Hockey League.[226] Boston was the site of the first game of the first modern World Series, in 1903. The series was played between the AL Champion Boston Americans and the NL champion Pittsburgh Pirates.[227][228] Persistent reports that the team was known in 1903 as the "Boston Pilgrims" appear to be unfounded.[229] Boston's first professional baseball team was the Red Stockings, one of the charter members of the National Association in 1871, and of the National League in 1876. The team played under that name until 1883, under the name Beaneaters until 1911, and under the name Braves from 1912 until they moved to Milwaukee after the 1952 season. Since 1966 they have played in Atlanta as the Atlanta Braves.[230]

The Celtics play at the TD Garden.
The TD Garden, formerly called the FleetCenter and built to replace the old, since-demolished Boston Garden, is adjoined to North Station and is the home of two major league teams: the Boston Bruins of the National Hockey League and the Boston Celtics of the National Basketball Association. The arena seats 18,624 for basketball games and 17,565 for ice hockey games. The Bruins were the first American member of the National Hockey League and an Original Six franchise.[231] The Boston Celtics were founding members of the Basketball Association of America, one of the two leagues that merged to form the NBA.[232] The Celtics have the distinction of having won more championships than any other NBA team, with seventeen.[233]
While they have played in suburban Foxborough since 1971, the New England Patriots of the National Football League were founded in 1960 as the Boston Patriots, changing their name after relocating. The team won the Super Bowl after the 2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, and 2016 seasons.[234] They share Gillette Stadium with the New England Revolution of Major League Soccer. The Boston Breakers of Women's Professional Soccer, which formed in 2009, play their home games at Dilboy Stadium in Somerville.[235] The Boston Storm of the United Women's Lacrosse League was formed in 2015.[236]

Harvard Stadium, the first collegiate athletic stadium built in the U.S.
The area's many colleges and universities are active in college athletics. Four NCAA Division I members play in the area—Boston College, Boston University, Harvard University, and Northeastern University. Of the four, only Boston College participates in college football at the highest level, the Football Bowl Subdivision. Harvard participates in the second-highest level, the Football Championship Subdivision. The Boston Cannons of the MLL play at Harvard Stadium.
One of the best known sporting events in the city is the Boston Marathon, the 26.2-mile (42.2 km) race which is the world's oldest annual marathon,[237] run on Patriots' Day in April. On April 15, 2013, two explosions killed three people and injured hundreds at the marathon.[83]
Another major annual event is the Head of the Charles Regatta, held in October.[238]
Parks and recreation

Boston Common seen from the Prudential Tower
Boston Common, located near the Financial District and Beacon Hill, is the oldest public park in the United States.[239] Along with the adjacent Boston Public Garden, it is part of the Emerald Necklace, a string of parks designed by Frederick Law Olmsted to encircle the city. The Emerald Necklace includes Jamaica Pond, Boston's largest body of freshwater, and Franklin Park, the city's largest park and home of the Franklin Park Zoo.[240] Another major park is the Esplanade, located along the banks of the Charles River. The Hatch Shell, an outdoor concert venue, is located adjacent to the Charles River Esplanade. Other parks are scattered throughout the city, with major parks and beaches located near Castle Island, in Charlestown and along the Dorchester, South Boston, and East Boston shorelines.[241]
Boston's park system is well-reputed nationally. In its 2013 ParkScore ranking, The Trust for Public Land reported that Boston was tied with Sacramento and San Francisco for having the third-best park system among the 50 most populous US cities.[242] ParkScore ranks city park systems by a formula that analyzes the city's median park size, park acres as percent of city area, the percent of residents within a half-mile of a park, spending of park services per resident, and the number of playgrounds per 10,000 residents.
Government and politics

The Massachusetts State House, seat of the Government of Massachusetts, on Beacon Hill
Boston has a strong mayor – council government system in which the mayor (elected every fourth year) has extensive executive power. Marty Walsh became Mayor in January 2014, his predecessor Thomas Menino's twenty-year tenure having been the longest in the city's history.[243]
The Boston City Council is elected every two years; there are nine district seats, and four citywide "at-large" seats.[244] The School Committee, which oversees the Boston Public Schools, is appointed by the mayor.[245]
In addition to city government, numerous commissions and state authorities—including the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, the Boston Public Health Commission, the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA), and the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport)—play a role in the life of Bostonians. As the capital of Massachusetts, Boston plays a major role in state politics.
The city has several federal facilities, including the John F. Kennedy Federal Office Building, the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building,[246] the John W. McCormack Post Office and Courthouse, the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston, the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, and the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. Both courts are housed in the John Joseph Moakley United States Courthouse.
Federally, Boston is split between two congressional districts. The northern three-fourths of the city is in the 7th district, represented by Mike Capuano since 1998. The southern fourth is in the 8th district, represented by Stephen Lynch.[247] Both are Democrats; a Republican has not represented a significant portion of Boston in over a century. The state's senior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Elizabeth Warren, first elected in 2012. The state's junior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Ed Markey, who was elected in 2013 to succeed John Kerry after Kerry's appointment and confirmation as the United States Secretary of State.
The city uses an algorithm created by the Walsh administration, called CityScore, to measure the effectiveness of various city services. This score is available on a public online dashboard and allows city managers in police, fire, schools, emergency management services, and 3-1-1 to take action and make adjustments in areas of concern.[248]
| Year | Democratic | Republican |
|---|---|---|
2016 | 80.6% 221,093 | 13.9% 38,087 |
2012 | 78.8% 200,190 | 19.3% 48,985 |
2008 | 79.0% 185,976 | 19.4% 45,548 |
2004 | 77.3% 160,884 | 21.4% 44,518 |
2000 | 71.7% 132,393 | 19.7% 36,389 |
1996 | 73.8% 125,529 | 19.6% 33,366 |
1992 | 62.4% 114,260 | 22.9% 41,868 |
1988 | 65.2% 122,349 | 33.2% 62,202 |
1984 | 63.4% 131,745 | 36.2% 75,311 |
1980 | 53.3% 95,133 | 32.9% 58,656 |
| Voter registration and party enrollment As of October 2012[update][250] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Number of voters | Percentage | |||
Democratic | 211,257 | 54.58% | |||
Republican | 25,903 | 6.69% | |||
Green-Rainbow | 686 | 0.17% | |||
| Unaffiliated | 147,813 | 38.19% | |||
| Total | 387,040 | 100% | |||
Media
Newspapers
The Boston Globe and the Boston Herald are two of the city's major daily newspapers. The city is also served by other publications such as Boston magazine, The Improper Bostonian, DigBoston, and the Boston edition of Metro. The Christian Science Monitor, headquartered in Boston, was formerly a worldwide daily newspaper but ended publication of daily print editions in 2009, switching to continuous online and weekly magazine format publications.[251]The Boston Globe also releases a teen publication to the city's public high schools, called Teens in Print or T.i.P., which is written by the city's teens and delivered quarterly within the school year.[252]
The city's growing Latino population has given rise to a number of local and regional Spanish-language newspapers. These include El Planeta (owned by the former publisher of The Boston Phoenix), El Mundo, and La Semana. Siglo21, with its main offices in nearby Lawrence, is also widely distributed.[253]
There are a number of weekly newspapers dedicated to Boston neighborhoods. Among them is South Boston Online, (founded in 1999) which appears in print and online, and covers events in South Boston and the Seaport District.
Various LGBT publications serve the city's large LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender) population such as The Rainbow Times, the only minority and lesbian-owned LGBT news magazine. Founded in 2006, The Rainbow Times is now based out of Boston, but serves all of New England.[254]
Radio and television
Boston is the largest broadcasting market in New England, with the radio market being the 9th largest in the United States.[255] Several major AM stations include talk radio WRKO, sports/talk station WEEI, and CBS Radio WBZ.[256] WBZ (AM) broadcasts a news radio format. A variety of commercial FM radio formats serve the area, as do NPR stations WBUR and WGBH. College and university radio stations include WERS (Emerson), WHRB (Harvard), WUMB (UMass Boston), WMBR (MIT), WZBC (Boston College), WMFO (Tufts University), WBRS (Brandeis University), WTBU (Boston University, campus and web only), WRBB (Northeastern University) and WMLN-FM (Curry College).
The Boston television DMA, which also includes Manchester, New Hampshire, is the 8th largest in the United States.[257] The city is served by stations representing every major American network, including WBZ-TV 4 and its sister station WSBK-TV 38 (the former a CBS O&O, the latter an MyNetwork TV affiliate), WCVB-TV 5 and its sister station WMUR-TV 9 (both ABC), WHDH 7 and its sister station WLVI 56 (the former an independent station, the latter a CW affiliate), WBTS-LD 8 (a NBC O&O), and WFXT 25 (Fox). The city is also home to PBS member station WGBH-TV 2, a major producer of PBS programs,[258] which also operates WGBX 44. Spanish-language television networks, including Azteca (WFXZ-CD 24), Univisión (WUNI 27), Telemundo (WNEU 60, a sister station to WBTS-LD), and UniMás (WUTF-DT 66), have a presence in the region, with WNEU and WUTF serving as network owned-and-operated stations. Most of the area's television stations have their transmitters in nearby Needham and Newton along the Route 128 corridor.[259] Six Boston television stations are carried by Canadian satellite television provider Bell TV and by cable television providers in Canada.
Film
Films have been made in Boston since as early as 1903, and it continues to be both a popular setting and a popular site for location shooting.[260][261]
Healthcare

Harvard Medical School, one of the most prestigious medical schools in the world
The Longwood Medical and Academic Area, adjacent to the Fenway district, is home to a large number of medical and research facilities, including Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston Children's Hospital, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Joslin Diabetes Center, and the Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences.[262]
Prominent medical facilities, including Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital are located in the Beacon Hill area. St. Elizabeth's Medical Center is in Brighton Center of the city's Brighton neighborhood. New England Baptist Hospital is in Mission Hill. The city has Veterans Affairs medical centers in the Jamaica Plain and West Roxbury neighborhoods.[263] The Boston Public Health Commission, an agency of the Massachusetts government, oversees health concerns for city residents.[264]Boston EMS provides pre-hospital emergency medical services to residents and visitors.
Many of Boston's medical facilities are associated with universities. The facilities in the Longwood Medical and Academic Area and in Massachusetts General Hospital are affiliated with Harvard Medical School.[265]Tufts Medical Center (formerly Tufts-New England Medical Center), located in the southern portion of the Chinatown neighborhood, is affiliated with Tufts University School of Medicine. Boston Medical Center, located in the South End neighborhood, is the primary teaching facility for the Boston University School of Medicine as well as the largest trauma center in the Boston area;[266] it was formed by the merger of Boston University Hospital and Boston City Hospital, which was the first municipal hospital in the United States.[267]
Infrastructure
Transportation

An MBTA Red Line train departing Boston for Cambridge. Bostonians depend heavily on public transit, with over 1.3 million Bostonians riding the city's buses and trains daily (2013).[268]

Leonard P. Zakim Bunker Hill Memorial Bridge crosses the Charles River from Downtown Boston.
Logan Airport, located in East Boston and operated by the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport), is Boston's principal airport.[269] Nearby general aviation airports are Beverly Municipal Airport to the north, Hanscom Field to the west, and Norwood Memorial Airport to the south. Massport also operates several major facilities within the Port of Boston, including a cruise ship terminal and facilities to handle bulk and container cargo in South Boston, and other facilities in Charlestown and East Boston.[270]
Downtown Boston's streets grew organically, so they do not form a planned grid,[271] unlike those in later-developed Back Bay, East Boston, the South End, and South Boston. Boston is the eastern terminus of I-90, which in Massachusetts runs along the Massachusetts Turnpike. The elevated portion of the Central Artery, which carried most of the through traffic in downtown Boston, was replaced with the O'Neill Tunnel during the Big Dig, substantially completed in early 2006.
With nearly a third of Bostonians using public transit for their commute to work, Boston has the fifth-highest rate of public transit usage in the country.[272] The city of Boston has a higher than average percentage of households without a car. In 2015, 35.4 percent of Boston households lacked a car, which decreased slightly to 33.8 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. Boston averaged 0.94 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8.[273] Boston's public transportation agency, the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates the oldest underground rapid transit system in the Americas, and is the fourth-busiest rapid transit system in the country,[18] with 65.5 miles (105 km) of track on four lines.[274] The MBTA also operates busy bus and commuter rail networks, and water shuttles.[274]

South Station, the busiest rail hub in New England, is a terminus of Amtrak and numerous MBTA rail lines.

Hubway bikes in Boston
Amtrak intercity rail to Boston is provided through four stations: South Station, North Station, Back Bay, and Route 128. South Station is a major intermodal transportation hub and is the terminus of Amtrak's Northeast Regional, Acela Express, and Lake Shore Limited routes, in addition to multiple MBTA services. Back Bay is also served by MBTA and those three Amtrak routes, while Route 128, located in the southwestern suburbs of Boston, is only served by the Acela Express and Northeast Regional.[275] Meanwhile, Amtrak's Downeaster to Brunswick terminates in North Station, and is the only Amtrak route to do so.[276]
Nicknamed "The Walking City", Boston hosts more pedestrian commuters than do other comparably populated cities. Owing to factors such as necessity, the compactness of the city and large student population, 13 percent of the population commutes by foot, making it the highest percentage of pedestrian commuters in the country out of the major American cities.[277] In 2011, Walk Score ranked Boston the third most walkable city in the United States.[278][279] As of 2015[update], Walk Score still ranks Boston as the third most walkable US city, with a Walk Score of 80, a Transit Score of 75, and a Bike Score of 70.[280]
Between 1999 and 2006, Bicycling magazine named Boston three times as one of the worst cities in the US for cycling;[281] regardless, it has one of the highest rates of bicycle commuting.[282] In 2008, as a consequence of improvements made to bicycling conditions within the city, the same magazine put Boston on its "Five for the Future" list as a "Future Best City" for biking,[283][284] and Boston's bicycle commuting percentage increased from 1% in 2000 to 2.1% in 2009.[285] The bikeshare program called Hubway launched in late July 2011,[286] logging more than 140,000 rides before the close of its first season.[287] The neighboring municipalities of Cambridge, Somerville, and Brookline joined the Hubway program in the summer of 2012.[288] In 2016, there are 1,461 bikes and 158 docking stations across the city.[289]PBSC Urban Solutions provides bicycles and technology for this bike-sharing system.[290]
In 2013, the Boston-Cambridge-Newton metropolitan statistical area (Boston MSA) had the seventh-lowest percentage of workers who commuted by private automobile (75.6 percent), with 6.2 percent of area workers traveling via rail transit. During the period starting in 2006 and ending in 2013, the Boston MSA had the greatest percentage decline of workers commuting by automobile (3.3 percent) among MSAs with more than a half-million residents.[291]
Twin towns and sister cities
The City of Boston has eleven official sister cities:[292]
 Kyoto, Japan (1959)
Kyoto, Japan (1959)
 Strasbourg, France (1960)
Strasbourg, France (1960)
 Barcelona, Spain (1980)
Barcelona, Spain (1980)
 Hangzhou, People's Republic of China (1982)
Hangzhou, People's Republic of China (1982)
 Padua, Italy (1983)
Padua, Italy (1983)
 Melbourne, Australia (1985)
Melbourne, Australia (1985)
 Beira, Mozambique (1990)
Beira, Mozambique (1990)
 Taipei, Taiwan (1996)
Taipei, Taiwan (1996)
 Sekondi-Takoradi, Ghana (2001)
Sekondi-Takoradi, Ghana (2001)
 Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom (2014)
Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom (2014)
 Praia, Cape Verde (2015)
Praia, Cape Verde (2015)
The City of Boston has formal partnership relationships through a Memorandum Of Understanding (MOU) with four additional cities or regions:
 Guangzhou, People's Republic of China (2014)[293]
Guangzhou, People's Republic of China (2014)[293]
 Lyon, France (2016)[294]
Lyon, France (2016)[294]
 Copenhagen, Denmark (2017)[295]
Copenhagen, Denmark (2017)[295]
 Mexico City, Mexico (2017)[296]
Mexico City, Mexico (2017)[296]
North West of Ireland, Ireland and United Kingdom (2017)[297]
In 1900, Americans from Boston bought a piece of land in Bellville, Western Cape, South Africa and developed it for residential purposes. In memory of their hometown, they called it Boston.
See also
Boston City League (high school athletic conference)- Boston nicknames
- Boston–Halifax relations
- List of diplomatic missions in Boston
- List of people from Boston
- List of tallest buildings in Boston
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Boston
- Boston bid for the 2024 Summer Olympics
Notes
^ On the New Style (modern) calendar, anniversaries fall on September 17.
^ On the New Style (modern) calendar, anniversaries of the original Old Style date fall on September 17.
^ The average number of days with a low at or below freezing is 94.
^ Seasonal snowfall accumulation has ranged from 9.0 in (22.9 cm) in 1936–37 to 110.6 in (2.81 m) in 2014–15.
^ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the expected highest and lowest temperature readings at any point during the year or given month) calculated based on data at said location from 1981 to 2010.
^ Official records for Boston were kept at downtown from January 1872 to December 1935, and at Logan Airport (KBOS) since January 1936.[106]
References
^ Thomas, G. Scott. "Boston's population stays flat, but still ranks as 10th-largest in U.S. (BBJ DataCenter)". bizjournals.com. Retrieved May 4, 2015..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abc "Population and Housing Occupancy Status: 2010 – State – County Subdivision, 2010 Census Redistricting Data (Public Law 94-171) Summary File". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 23, 2011.
^ abc "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 25, 2018.
^ "Alphabetically sorted list of Census 2000 Urbanized Areas". United States Census Bureau, Geography Division. Archived from the original (TXT) on June 13, 2002. Retrieved April 11, 2009.
^ "Table 1. Annual Estimates of the Population of Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2011 (CBSA-EST2011-01)". United States Census Bureau, Population Division. Archived from the original (CSV) on April 27, 2012. Retrieved January 18, 2013.
^ "Table 2. Annual Estimates of the Population of Combined Statistical Areas: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2011 (CBSA-EST2011-02)". United States Census Bureau, Population Division. Archived from the original (CSV) on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 18, 2013.
^ "ZIP Code Lookup – Search By City". United States Postal Service. Archived from the original on September 3, 2007. Retrieved April 20, 2009.
^ "Population and Housing Occupancy Status: 2010 – State – County Subdivision 2010 Census Redistricting Data (Public Law 94-171) Summary File". United States Census Bureau. 2010. Retrieved March 4, 2013.
^ "List of intact or abandoned Massachusetts county governments". sec.state.ma.us. Secretary of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved October 31, 2016.
^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2016 Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2016 Population Estimates Boston-Worcester-Providence, MA-RI-NH-CT CSA". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
^ Banner, David. "Boston History – The History of Boston, Massachusetts". SearchBoston. Archived from the original on March 15, 2009. Retrieved April 20, 2009.
^ ab Kennedy 1994, pp. 11–12.
^ ab "About Boston". City of Boston. Retrieved May 1, 2016.
^ ab Morris 2005, p. 8.
^ "Top 25 Most Visited Tourist Destinations in America". The Travelers Zone. May 10, 2008. Retrieved February 14, 2013.
^ abc "BPS at a Glance". Boston Public Schools. March 14, 2007. Archived from the original on April 3, 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ ab Hull 2011, p. 42.
^ "World Reputation Rankings". April 21, 2016. Retrieved May 12, 2016.
^ "Venture Investment - Regional Aggregate Data". National Venture Capital Association and PricewaterhouseCoopers. Retrieved April 22, 2016.
^ ab Kirsner, Scott (July 20, 2010). "Boston is #1 ... But will we hold on to the top spot? – Innovation Economy". The Boston Globe. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
^ Innovation that Matters 2016 (Report). US Chamber of Commerce. 2016.
^ [1] Accessed October 7, 2018.
^ "The Boston Economy in 2010" (PDF). Boston Redevelopment Authority. January 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 30, 2012. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ "Transfer of Wealth in Boston" (PDF). The Boston Foundation. March 2013. Retrieved December 6, 2015.
^ "Boston Ranked Most Energy-Efficient City in the United States". City Government of Boston. September 18, 2013. Retrieved December 6, 2015.
^ "In the wake of the Ghost Ship fire, examining Oakland's 'staggering' rent hikes". December 10, 2016. Retrieved December 12, 2016.
^ ab Heudorfer, Bonnie; Bluestone, Barry. "The Greater Boston Housing Report Card" (PDF). Center for Urban and Regional Policy (CURP), Northeastern University. p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 8, 2006. Retrieved December 12, 2016.
^ Tom Acitelli (December 7, 2016). "Which Boston neighborhoods will gentrify next?". Vox Media. Retrieved December 12, 2016.
^ "Quality of Living global city rankings 2010 – Mercer survey". Mercer. May 26, 2010. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 20, 2011.
^ Drake, Samuel Adams (1872). Old Landmarks and Historic Personages of Boston. p. 6.
^ "Archives Guide ~ Town of Boston". City of Boston. 2013. Archived from the original on April 20, 2013. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
^
"Archaeology of the Central Artery Project: Highway to the Past". Commonwealth Museum – Massachusetts Historical Commission. 2007. Retrieved April 6, 2007.
^ Christopher 2006, p. 46.
^ ""Growth" to Boston in its Heyday, 1640s to 1730s" (PDF). Boston History & Innovation Collaborative. 2006. p. 2. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ abcde Smith, Robert W. (2005). Encyclopedia of the New American Nation (1st ed.). Detroit, MI: Charles Scribners & Sons. pp. 214–219. ISBN 978-0684313467.
^ ab Bunker, Nick (2014). An Empire on the Edge: How Britain Came to Fight America. Knopf. ISBN 978-0307594846.
^ Dawson, Henry B. (1858). Battles of the United States, by sea and land: embracing those of the Revolutionary and Indian Wars, the War of 1812, and the Mexican War; with important official documents. New York, NY: Johnson, Fry & Company.
^ Morris 2005, p. 7.
^ Morgan, Edmund S. (1946). "Thomas Hutchinson and the Stamp Act". The New England Quarterly. 21 (4): 459–492. doi:10.2307/361566.
^ ab Frothingham, Jr, Richard (1851). History of the Siege of Boston and of the Battles of Lexington, Concord, and Bunker Hill. Little and Brown.
^ ab French, Allen (1911). The Siege of Boston. McMillan.
^ McCullough, David (2005). 1776. New York, NY: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-2671-4.
^ "New England's hidden history". Boston.com. Retrieved May 22, 2016.
^ "Colonial Boston". University Archives. Archived from the original on February 7, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
^ abc "Boston Economy". City-Data.com. Advameg Inc. 2007. Retrieved June 20, 2007.
^ Kennedy 1994, p. 46.
^ Whitehill, Walter Muir (1968). Boston: A Topographical History (Second ed.). pp. 81–84.
^ "Home page" (Exhibition at Boston Public Library and Massachusetts Historical Society). Forgotten Chapters of Boston's Literary History. The Trustees of Boston College. March 28 – July 30, 2012. Retrieved May 22, 2012.
^ "An Interactive Map of Literary Boston: 1794–1862" (Exhibition). Forgotten Chapters of Boston's Literary History. The Trustees of Boston College. March 28 – July 30, 2012. Retrieved May 22, 2012.
^ Kennedy 1994, p. 44.
^ Dilworth, Richardson. Cities in American Political History. Sage Publications. p. 28.
^ "Boston African American National Historic Site". National Park Service. April 28, 2007. Retrieved May 8, 2007.
^ "Fugitive Slave Law". The Massachusetts Historical Society. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
^ "The "Trial" of Anthony Burns". The Massachusetts Historical Society. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
^ "150th Anniversary of Anthony Burns Fugitive Slave Case". Suffolk University. April 24, 2004. Archived from the original on May 20, 2008. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
^ ab State Street Trust Company; Walton Advertising & Printing Company (1922). Boston: one hundred years a city (TXT). 2. Boston: State Street Trust Company. Retrieved April 20, 2009.
^
"People & Events: Boston's Immigrant Population". WGBH/PBS Online (American Experience). 2003. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. Retrieved May 4, 2007.
^ "Immigration Records". The National Archives. Archived from the original on January 14, 2009. Retrieved January 7, 2009.
^ Puleo, Stephen (2007). "Epilogue: Today". The Boston Italians (illustrated ed.). Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-5036-1. Retrieved May 16, 2009.
^ "Boston People". City-Data.com. Advameg Inc. 2007. Retrieved May 5, 2007.
^ Bolino 2012, pp. 285–286.
^ ab "The History of Land Fill in Boston". iBoston.org. 2006. Retrieved January 9, 2006.. Also see Howe, Jeffery (1996). "Boston: History of the Landfills". Boston College. Archived from the original on April 10, 2007. Retrieved April 30, 2007.
^ Historical Atlas of Massachusetts. University of Massachusetts. 1991. p. 37.
^ Holleran, Michael (2001). "Problems with Change". Boston's Changeful Times: Origins of Preservation and Planning in America. The Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-8018-6644-9. Retrieved August 22, 2010.
^ "Boston's Annexation Schemes.; Proposal To Absorb Cambridge And Other Near-By Towns" (PDF). The New York Times. March 26, 1892. p. 11. Archived from the original on March 27, 1892. Retrieved August 21, 2010.
^ Rezendes, Michael (October 13, 1991). "Has the time for Chelsea's annexation to Boston come? The Hub hasn't grown since 1912, and something has to follow that beleaguered community's receivership". The Boston Globe. p. 80. Retrieved August 22, 2010.
^ Estes, Andrea; Cafasso, Ed (September 9, 1991). "Flynn offers to annex Chelsea". Boston Herald. p. 1. Retrieved August 22, 2010.
^ Bluestone & Stevenson 2002, p. 13.
^ Collins, Monica (August 7, 2005). "Born Again". The Boston Globe. Retrieved May 8, 2007.
^ Roessner, Jane (2000). A Decent Place to Live: from Columbia Point to Harbor Point – A Community History. Boston: Northeastern University Press. p. 80. ISBN 978-1-55553-436-3.
^ Cf. Roessner, p.293. "The HOPE VI housing program, inspired in part by the success of Harbor Point, was created by legislation passed by Congress in 1992."
^ Kennedy 1994, p. 195.
^ Kennedy 1994, pp. 194–195.
^
Feeney, Mark; Mehegan, David (April 15, 2005). "Atlantic, 148-year institution, leaving city". The Boston Globe. Retrieved March 31, 2007.
^ "FleetBoston, Bank of America Merger Approved by Fed". The Boston Globe. March 9, 2004. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ Abelson, Jenn; Palmer, Jr., Thomas C. (July 29, 2005). "It's Official: Filene's Brand Will Be Gone". The Boston Globe. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ Glaberson, William (June 11, 1993). "Largest Newspaper Deal in U.S. – N.Y. Times Buys Boston Globe for $1.1 Billion". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. p. B-12. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ Hampson, Rick (April 19, 2005). "Studies: Gentrification a boost for everyone". USA Today. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
^ "Cost of Living Index for Selected U.S. Cities, 2005". Information Please Database. Pearson Education. 2007. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
^ "Worldwide Cost of Living Survey 2011 – City Ranking". Mercer. July 12, 2011. Retrieved February 21, 2013.
^ "2011 Quality of Living worldwide city rankings – Mercer survey". Mercer. November 29, 2011. Archived from the original on November 28, 2012. Retrieved January 29, 2012.
^ ab McConville, Christine (April 23, 2013). "Marathon injury toll jumps to 260". Boston Herald. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
^ "The life and death of Boston's Olympic bid". August 4, 2016.
^ "Elevation data – Boston". U.S. Geological Survey. 2007.
^ "Bellevue Hill, Massachusetts". Peakbagger.com.
^ United States Embassy. "Boston, Massachusetts: America's City of Firsts". Retrieved December 29, 2015.
^ "Kings Chapel Burying Ground, USGS Boston South (MA) Topo Map". TopoZone. 2006. Archived from the original on June 29, 2012. Retrieved January 6, 2016.
^ "Official list of Boston neighborhoods". Cityofboston.gov. March 24, 2011. Retrieved September 1, 2012.
^ Shand-Tucci, Douglass (1999). Built in Boston: City & Suburb, 1800–2000 (2 ed.). University of Massachusetts Press. pp. 11, 294–299. ISBN 978-1-55849-201-1.
^ "Boston Skyscrapers". Emporis.com. 2005. Retrieved May 15, 2005.
^ Hull 2011, p. 91.
^ "Our History". South End Historical Society. 2013. Retrieved February 17, 2013.
^ Morris 2005, pp. 54, 102.
^ "World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated". University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna. November 6, 2008. Archived from the original on September 6, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2018.
^ abc "Weather". City of Boston Film Bureau. 2007. Archived from the original on February 1, 2013. Retrieved April 29, 2007.
^ "USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map". United States Department of Agriculture. Archived from the original on February 27, 2014. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
^ abcdefg "NowData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2017-02-25.
^ "Threaded Extremes". National Weather Service. Retrieved June 28, 2010.
^
"Massachusetts – Climate". City-Data.com. Advameg Inc. 2005. Retrieved April 29, 2007.
^
"May in the Northeast". Intellicast.com. 2003. Archived from the original on April 29, 2007. Retrieved April 29, 2007.
^
Wangsness, Lisa (October 30, 2005). "Snowstorm packs October surprise". The Boston Globe. Retrieved April 29, 2007.
^
Ryan, Andrew (July 11, 2007). "Sea breeze keeps Boston 25 degrees cooler while others swelter". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on November 7, 2013. Retrieved March 31, 2009.
^
Ryan, Andrew (June 9, 2008). "Boston sea breeze drops temperature 20 degrees in 20 minutes". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved March 31, 2009.
^ "Tornadoes in Massachusetts". Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved February 24, 2013.
^ ThreadEx
^ "Station Name: MA BOSTON LOGAN INTL AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2013-03-24.
^ "WMO Climate Normals for BOSTON/LOGAN INT'L AIRPORT, MA 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
^ "Total Population (P1), 2010 Census Summary File 1". American FactFinder, All County Subdivisions within Massachusetts. United States Census Bureau. 2010.
^ "Massachusetts by Place and County Subdivision - GCT-T1. Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1990 Census of Population, General Population Characteristics: Massachusetts" (PDF). US Census Bureau. December 1990. Table 76: General Characteristics of Persons, Households, and Families: 1990. 1990 CP-1-23. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1980 Census of the Population, Number of Inhabitants: Massachusetts" (PDF). US Census Bureau. December 1981. Table 4. Populations of County Subdivisions: 1960 to 1980. PC80-1-A23. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1950 Census of Population" (PDF). Bureau of the Census. 1952. Section 6, Pages 21-10 and 21-11, Massachusetts Table 6. Population of Counties by Minor Civil Divisions: 1930 to 1950. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1920 Census of Population" (PDF). Bureau of the Census. Number of Inhabitants, by Counties and Minor Civil Divisions. Pages 21-5 through 21-7. Massachusetts Table 2. Population of Counties by Minor Civil Divisions: 1920, 1910, and 1920. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1890 Census of the Population" (PDF). Department of the Interior, Census Office. Pages 179 through 182. Massachusetts Table 5. Population of States and Territories by Minor Civil Divisions: 1880 and 1890. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1870 Census of the Population" (PDF). Department of the Interior, Census Office. 1872. Pages 217 through 220. Table IX. Population of Minor Civil Divisions, &c. Massachusetts. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1860 Census" (PDF). Department of the Interior, Census Office. 1864. Pages 220 through 226. State of Massachusetts Table No. 3. Populations of Cities, Towns, &c. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1850 Census" (PDF). Department of the Interior, Census Office. 1854. Pages 338 through 393. Populations of Cities, Towns, &c. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ "1950 Census of Population" (PDF). 1: Number of Inhabitants. Bureau of the Census. 1952. Section 6, Pages 21–07 through 21-09, Massachusetts Table 4. Population of Urban Places of 10,000 or more from Earliest Census to 1920. Retrieved July 12, 2011.
^ United States Census Bureau. "Table 3. Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places in Massachusetts: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2011 (SUB-EST2011-03-25)". Archived from the original on March 9, 2013. Retrieved January 18, 2013.
^ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
^ "Boston's Population Doubles – Every Day" (PDF). Boston Redevelopment Authority – Insight Reports. December 1996. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 23, 2013. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
^ ab "Boston city, Massachusetts—DP02, Selected Social Characteristics in the United States 2007–2011 American Community Surver 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. 2011. Archived from the original on August 15, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
^ "Boston city, Massachusetts—DP03. Selected Economic Characteristics 2007–2011 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. 2011. Archived from the original on September 16, 2013. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
^ abcd "Massachusetts – Race and Hispanic Origin for Selected Cities and Other Places: Earliest Census to 1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on August 6, 2012. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
^ "Boston, Massachusetts". Sperling's BestPlaces. 2008. Archived from the original on March 18, 2008. Retrieved April 6, 2008.
^ Jonas, Michael (August 3, 2008). "Majority-minority no more?". The Boston Globe. Retrieved November 30, 2009.
^ "Boston 2010 Census: Facts & Figures". Boston Redevelopment Authority News. March 23, 2011. Archived from the original on January 18, 2012. Retrieved February 13, 2012.
^ "QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau.
^ ab From 15% sample
^ "Boston city, Massachusetts QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". census.gov.
^ "Massachusetts QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". census.gov.
^ "Boston city, Massachusetts—DP02, Selected Social Characteristics in the United States 2007–2011 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. 2011. Archived from the original on August 15, 2014. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
^ "SELECTED POPULATION PROFILE IN THE UNITED STATES 2011-2013 American Community Survey 3-Year Estimates - Chinese alone, Boston city, Massachusetts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 15, 2016.
^ "New Bostonians 2009" (PDF). Boston Redevelopment Authority/Research Division. October 2009. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
^ Data Access and Dissemination Systems (DADS). "American FactFinder – Results". census.gov. Archived from the original on December 18, 2014.
^ "PEOPLE REPORTING ANCESTRY 2012-2016 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved August 25, 2018.
^ "ACS DEMOGRAPHIC AND HOUSING ESTIMATES 2012-2016 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved August 25, 2018.
^ "SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS 2008–2012 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved March 19, 2014.
^ "ACS DEMOGRAPHIC AND HOUSING ESTIMATES 2008–2012 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved March 19, 2014.
^ "HOUSEHOLDS AND FAMILIES 2008–2012 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved March 19, 2014.
^ Major U.S. metropolitan areas differ in their religious profiles, Pew Research Center
^ "America's Changing Religious Landscape". Pew Research Center: Religion & Public Life. May 12, 2015.
^ "The Association of Religion Data Archives - Maps & Reports".
^ ab "2015 Greater Boston Jewish Community Study" (PDF). Maurice and Marilyn Cohen Center for Modern Jewish Studies, Brandeis University. Retrieved November 24, 2016.
^ "Fortune 500 Companies 2018: Who Made The List". Fortune. Meredith Corporation. Retrieved October 1, 2018.
^ MA Executive Office of Labor and Workforce Development: Largest 200 Employers in Suffolk County (2017). Retrieved on May 10, 2017.
^ "Industry by Occupation for the Civilian Employed Population 16 Years and Over [Boston-Cambridge-Nashua, MA-NH Metropolitan NECTA]". US Census Bureau. 2016.
^ Florida, Richard (May 8, 2012). "What Is the World's Most Economically Powerful City?". The Atlantic Monthly Group. Retrieved February 21, 2013.
^ "Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025". Pricewaterhouse Coopers. Archived from the original on May 13, 2011. Retrieved November 20, 2009.
^ McSweeney, Denis M. "The prominence of Boston area colleges and universities" (PDF). Retrieved April 25, 2014.
^ "Leadership Through Innovation: The History of Boston's Economy" (PDF). Boston Redevelopment Authority. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 6, 2010. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
^ "Milken report: The Hub is still tops in life sciences". The Boston Globe. May 19, 2009. Archived from the original on May 23, 2009. Retrieved August 25, 2009.
^ "Top 100 NIH Cities". SSTI.org. 2004. Retrieved February 19, 2007.
^ "Boston: The City of Innovation". TalentCulture. August 2, 2010. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
^ "Venture Investment - Regional Aggregate Data". National Venture Capital Association. Retrieved January 17, 2016.
^ "Tourism Statistics & Reports". Greater Boston Convention and Visitors Bureau. 2009–2011. Retrieved February 20, 2013.
^ "GBCVB, Massport Celebrate Record Number of International Visitors in 2014". Greater Boston Convention and Visitors Bureau. August 21, 2015. Retrieved January 17, 2016.
^ CASE STUDY: City of Boston, Massachusetts;Cost Plans for Governments
^ "About the Port – History". Massport. 2007. Archived from the original on July 2, 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ "The Global Financial Centres Index 21" (PDF). China Development Institute. March 2017.
^ Yeandle, Mark (March 2011). "The Global Financial Centres Index 9" (PDF). The Z/Yen Group. p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 14, 2012. Retrieved January 31, 2013.
^ "Top 10 Cities For A Career In Finance". Investopedia.com. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
^ "History of Boston's Economy – Growth and Transition 1970–1998" (PDF). Boston Redevelopment Authority. November 1999. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 23, 2013. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
^ Morris, Marie (2006). Frommer's Boston 2007 (2 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-470-08401-4.
^ "General Electric To Move Corporate Headquarters To Boston". CBS Local Media. January 13, 2016. Retrieved January 15, 2016.
^ "Top shoe brands, like Reebok and Converse, move headquarters to Boston". Omaha.com. Retrieved January 19, 2017.
^ "Reebok Is Moving to Boston". Boston Magazine. Retrieved January 19, 2017.
^ "BPS at a glance" (PDF). bostonpublicschools.org.
^ "Metco Program". Massachusetts Department of Elementary & Secondary Education. June 16, 2011. Retrieved February 20, 2013.
^ "Academic Ranking of World Universities 2015". ShanghaiRanking Consultancy. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
^ "CWUR 2015 – World University Rankings". Center for World University Rankings. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
^ "Brainpower Triangle Cambridge Massachusetts - New Media Technology and Tech Clusters". the New Media. Archived from the original on July 14, 2016. Retrieved May 8, 2016.
^ Kladko, Brian (April 20, 2007). "Crimson Tide". Boston Business Journal. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ "The MIT Press: When MIT Was "Boston Tech"". The MIT Press. 2013. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ "Boston Campus Map". Tufts University. 2013. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
^ "MEMBER INSTITUTIONS AND YEARS OF ADMISSION". Association of American Universities. Retrieved July 17, 2014.
^ Jan, Tracy (April 2, 2014). "Rural states seek to sap research funds from Boston". The Boston Globe.
^ "City of Boston". Boston University. 2014. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 9, 2014.
^ "The Largest Employers in the City of Boston" (PDF). Boston Redevelopment Authority. 1996–1997. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 23, 2013. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
^ "Northeastern University". U.S. News and World Reports. 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ "Suffolk University". U.S. News and World Reports. 2013. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
^ Laczkoski, Michelle (February 27, 2006). "BC outlines move into Allston-Brighton". The Daily Free Press. Boston University. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
^ "Boston By The Numbers". City of Boston. Retrieved June 9, 2014.
^ "History of NESL". New England School of Law. 2010. Retrieved October 17, 2010.
^ "Emerson College". U.S. News and World Reports. 2013. Archived from the original on January 30, 2013. Retrieved February 6, 2013.
^ "A Brief History of New England Conservatory". New England Conservatory of Music. 2007. Archived from the original on November 20, 2008. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ Everett, Carole J. (2009). College Guide for Performing Arts Majors: The Real-World Admission Guide for Dance, Music, and Theater Majors. Peterson's. pp. 199–200. ISBN 978-0-7689-2698-9.
^ Winship, Christopher (March 2002). "End of a Miracle?" (PDF). Harvard University. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 22, 2012. Retrieved February 19, 2007.
^ "2008 Crime Summary Report" (PDF). The Boston Police Department Office Research and Development. 2008. p. 5. Retrieved February 20, 2013.
^ Ransom, Jan (December 31, 2016). "Boston's homicides up slightly, shootings down". Boston Globe. Retrieved December 31, 2016.
^ Vorhees 2009, p. 52.
^ Vorhees 2009, pp. 148–151.
^ Baker, Billy (May 25, 2008). "Wicked good Bostonisms come, and mostly go". The Boston Globe. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
^ Vennochi, Joan (October 24, 2017). "NAACP report shows a side of Boston that Amazon isn't seeing". The Boston Globe. Retrieved October 24, 2017.
^ "LCP Art & Artifacts". Library Company of Philadelphia. 2007.
^ ab Bross, Tom; Harris, Patricia; Lyon, David (2008). Boston. London: Dorling Kindersley. p. 22.
^ Bross, Tom; Harris, Patricia; Lyon, David (2008). Boston. London: Dorling Kindersley. p. 59.
^ "The world's greatest orchestras". Gramophone.
^ Cox, Trevor (March 5, 2015). "10 of the world's best concert halls". The Guardian.
^ ab Hull 2011, p. 175.
^ "Who We Are". Handel and Haydn Society. 2007. Archived from the original on April 27, 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ Hull 2011, pp. 53–55.
^ Hull 2011, p. 207.
^ "Boston Harborfest – About". Boston Harborfest Inc. 2013. Archived from the original on May 6, 2013. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ "Our Story: About Us". Boston 4 Celebrations Foundation. 2010. Archived from the original on February 23, 2013. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ Hull 2011, pp. 104–108.
^ Ouroussoff, Nicolai (December 8, 2006). "Expansive Vistas Both Inside and Out". The New York Times. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ "Art Galleries".
^ "Art Galleries on Newbury Street, Boston".
^ "History of The Boston Athenaeum". Boston Athenæum. 2012. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ Hull 2011, p. 164.
^ "First Church in Boston History". First Church in Boston. Retrieved November 12, 2013.
^ Riess, Jana (2002). The Spiritual Traveler: Boston and New England: A Guide to Sacred Sites and Peaceful Places. Hidden Spring. pp. 64–125. ISBN 978-1-58768-008-3.
^ "EPA AirCompare Historical Profile". Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved December 26, 2014.
^ "The Green District Allston". Encore Realty.
^ ab "About Your Community". goodguide.com.
^ "Where Has All the Water Gone? Left Piles Rotting ..." bsces.org. Archived from the original on November 28, 2014.
^ Groundwater, CityofBoston.gov
^ "Your Drinking Water: Massachusetts Water Resources Authority, 2006 Drinking Water Report" (Press release). Massachusetts Water Resources Authority. June 19, 2007.
^ Abraham, Yvonne (July 22, 2007). "Pure water, right on Tap". The Boston Globe. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
^ Zezima, Katie (June 16, 2011). "Long Memory or Short, Boston Fans Savor Success". The New York Times. Retrieved June 16, 2011.
^ "The New Title Town USA - Video - SI.com". Sports Illustrated. February 4, 2012. Archived from the original on February 5, 2012. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
^ "SPORTS CHART OF THE DAY: Boston Is The New "Title Town"". Business Insider. June 16, 2011. Retrieved January 22, 2013.
^ Arsenault, Mark (November 23, 2014). "Boston bidders hope time is right for frugal Games". The Boston Globe.
^ "Fenway Park". ESPN. 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ Abrams, Roger I. (February 19, 2007). "Hall of Fame third baseman led Boston to first AL pennant". National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum. Archived from the original on September 2, 2007. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
^ "1903 World Series – Major League Baseball: World Series History". Major League Baseball at MLB.com. 2007. Retrieved February 18, 2007. Please note: This source, like many others, uses the erroneous "Pilgrims" name that is debunked by the Nowlin reference following.
^ Bill Nowlin (2008). "The Boston Pilgrims Never Existed". Baseball Almanac. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
^ "Braves History". Atlanta Brave (MLB). 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ "National Hockey League (NHL) Expansion History". Rauzulu's Street. 2004. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
^ "NBA History – NBA Growth Timetable". Basketball.com. Archived from the original on March 31, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
^ "NBA Finals: All-Time Champions". NBA. 2007. Retrieved February 20, 2007.
^ "The History of the New England Patriots". New England Patriots. 2007. Archived from the original on May 19, 2011. Retrieved April 29, 2007.
^ Springer, Shira (April 11, 2009). "Breakers shoot for foothold in local market". The Boston Globe. Retrieved June 27, 2009.
^ "Play It Forward Sport and STX Announce Semi-Professional Women's Lacrosse League" (Press release). www.playitforwardsport.org. May 21, 2015. Archived from the original on June 25, 2016. Retrieved June 1, 2016.
^ "B.A.A. Boston Marathon Race Facts". Boston Athletic Association. 2007. Retrieved April 29, 2007.
^ "Crimson Rules College Lightweights at Head of the Charles". Harvard Athletic Communications. October 23, 2011. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
^ Morris 2005, p. 61.
^ "Franklin Park". City of Boston. 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ "Open Space Plan 2008–2014: Section 3 Community Setting" (PDF). City of Boston Parks & Recreation. January 2008. Retrieved February 21, 2013.
^ Randall, Eric. "Boston has one of the best park systems in the country". June 5, 2013. Boston Magazine. Retrieved on July 15, 2013.
^ Patton, Zach (January 2012). "The Boss of Boston: Mayor Thomas Menino". Governing. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ "Boston City Charter" (PDF). City of Boston. July 2007. p. 59. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ "The Boston Public Schools at a Glance: School Committee". Boston Public Schools. March 14, 2007. Archived from the original on April 3, 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ "Massachusetts Real Estate Portfolio". United States General Services Administration. Retrieved March 11, 2014.
^ "Massachusetts's Representatives – Congressional District Maps". GovTrack.us. 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ Irons, Meghan E. (August 17, 2016). "City Hall is always above average – if you ask City Hall". The Boston Globe. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
^ "Massachusetts Election Statistics". Retrieved September 26, 2018.
^ "The Commonwealth of Massachusetts: Enrollment Breakdown as of 10/17/2012" (PDF). Massachusetts Elections Division. November 1, 2012. p. 16. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
^ "Editor's message about changes at the Monitor". The Christian Science Monitor. March 27, 2009. Retrieved July 13, 2009.
^ "WriteBoston – T.i.P". City of Boston. 2007. Archived from the original on February 7, 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ Diaz, Johnny (September 6, 2008). "A new day dawns for a Spanish-language publication". The Boston Globe. Retrieved February 4, 2013.
^ Diaz, Johnny (January 26, 2011). "Bay Windows acquires monthly paper". The Boston Globe. Retrieved February 4, 2013.
^ "Arbitron – Market Ranks and Schedule, 1–50". Arbitron. Fall 2005. Retrieved February 18, 2007.
^ "AM Broadcast Classes; Clear, Regional, and Local Channels". Federal Communications Commission. January 20, 2012. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved February 20, 2013.
^ "Nielsen Survey" (PDF). nielsen.com.
^ "About Us: From our President". WGBH. 2013. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
^ "The Route 128 tower complex". The Boston Radio Archives. 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ "Made In Mass". MAFilm.org. MA Film Office. Retrieved February 2, 2015.
^ "New England Film". NewEnglandFilm.com. NewEnglandFilm. Retrieved February 8, 2015.
^ "About MASCO". MASCO – Medical Academic and Scientific Community Organization. 2007. Retrieved May 6, 2012.
^ "Facility Listing Report". United States Department of Veterans Affairs. 2007. Archived from the original on March 24, 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
^ "About BPHC – The Nation's First Health Department". Boston Public Health Commission. 2013. Archived from the original on April 17, 2009. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ "Hospital Overview". Massachusetts General Hospital. 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ "Boston Medical Center – Facts" (PDF). Boston Medical Center. November 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 3, 2007. Retrieved February 21, 2007.
^ "Boston Medical Center". Children's Hospital Boston. 2007. Archived from the original on August 15, 2007. Retrieved November 14, 2007.
^ "Statistics" (PDF). apta.com.
^ "About Logan". Massport. 2007. Archived from the original on May 21, 2007. Retrieved May 9, 2007.
^ "About Port of Boston". Massport. 2013. Archived from the original on February 25, 2013. Retrieved March 3, 2013.
^ Shurtleff, Arthur A. (January 1911). "The Street Plan of the Metropolitan District of Boston". Landscape Architecture 1: 71–83. Archived from the original on October 29, 2010.
^ "Census and You" (PDF). US Census Bureau. January 1996. p. 12. Retrieved February 19, 2007.
^ "Car Ownership in U.S. Cities Data and Map". Governing. Retrieved May 3, 2018.
^ ab "Boston: Light Rail Transit Overview". Light Rail Progress. May 2003. Retrieved February 19, 2007.
^ "Westwood—Route 128 Station, MA (RTE)". Amtrak. 2007. Archived from the original on August 22, 2008. Retrieved May 9, 2007.
^ "Boston—South Station, MA (BOS)". Amtrak. 2007. Archived from the original on April 18, 2008. Retrieved May 9, 2007.
^ Of cities over 250,000 "Carfree Database Results – Highest percentage (Cities over 250,000)". Bikes at Work Inc. 2007. Retrieved February 26, 2007.
^ Said, Carolyn (July 20, 2011). "S.F., Oakland in top 10 most walkable U.S. cities". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved July 20, 2011.
^ "The 10 most walkable U.S. cities". MarketWatch. 2011. Retrieved July 20, 2011.
^ "Boston". Walk Score. Walk Score. Retrieved June 3, 2015.
^ Zezima, Katie (August 8, 2009). "Boston Tries to Shed Longtime Reputation as Cyclists' Minefield". The New York Times. Retrieved May 24, 2015.
^ "Bicycle Commuting and Facilities in Major U.S. Cities: If You Build Them, Commuters Will Use Them – Another Look" (PDF). Dill bike facilities. 2003. p. 5. Retrieved April 4, 2007.
^ Katie Zezima (August 9, 2009). "Boston Tries to Shed Longtime Reputation as Cyclists' Minefield". The New York Times. Retrieved August 16, 2009.
^ "A Future Best City: Boston". Rodale Inc. Archived from the original on February 11, 2010. Retrieved August 16, 2009.
^ "Is Bicycle Commuting Really Catching On? And if So, Where?". The Atlantic Media Company. Retrieved December 28, 2011.
^ Moskowitz, Eric (April 21, 2011). "Hub set to launch bike-share program". The Boston Globe. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
^ Fox, Jeremy C. (March 29, 2012). "Hubway bike system to be fully launched by April 1". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on May 14, 2012. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
^ Franzini, Laura E. (August 8, 2012). "Hubway expands to Brookline, Somerville, Cambridge". The Boston Globe. Retrieved March 15, 2013.
^ "Hubway Bikes Boston | PBSC". Retrieved August 3, 2016.
^ RedEye. "Divvy may test-drive helmet vending machines at stations". Retrieved August 3, 2016.
^ McKenzie, Brian (August 2015). "Who Drives to Work? Commuting by Automobile in the United States: 2013" (PDF). American Survey Reports. Retrieved December 26, 2017.
^ "Sister Cities". City of Boston. July 18, 2017. Retrieved July 20, 2018.
^ "Friendly Cities". Guangzhou People's Government. Retrieved July 20, 2018.
^ City of Boston (February 10, 2016). "MAYOR WALSH SIGNS MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING WITH LYON, FRANCE VICE-MAYOR KARIN DOGNIN-SAUZE". City of Boston. Retrieved July 20, 2018.
^ "CITY OF CAMBRIDGE JOINS BOSTON, COPENHAGEN IN CLIMATE MEMORANDUM OF COLLABORATION". City of Cambridge. Retrieved July 20, 2017.
^ Boston City TV (April 4, 2017). "Memorandum of Understanding with Mexico City's Mayor Mancera - Promo". City of Boston. Retrieved July 20, 2018.
^ Derry City & Strabane District Council (November 17, 2017). "Ireland North West and City of Boston sign MOU". Derry City & Strabane District Council. Retrieved July 20, 2018.
Sources
Bluestone, Barry; Stevenson, Mary Huff (2002). The Boston Renaissance: Race, Space, and Economic Change in an American Metropolis. Russell Sage Foundation. ISBN 978-1-61044-072-1.
Bolino, August C. (2012). Men of Massachusetts: Bay State Contributors to American Society. iUniverse. ISBN 978-1-4759-3376-5.
Christopher, Paul J. (2006). 50 Plus One Greatest Cities in the World You Should Visit. Encouragement Press, LLC. ISBN 978-1-933766-01-0.
Hull, Sarah (2011). The Rough Guide to Boston (6 ed.). Penguin. ISBN 978-1-4053-8247-2.
Kennedy, Lawrence W. (1994). Planning the City Upon a Hill: Boston Since 1630. University of Massachusetts Press. ISBN 978-0-87023-923-6.
Morris, Jerry (2005). The Boston Globe Guide to Boston. Globe Pequot. ISBN 978-0-7627-3430-6.
Vorhees, Mara (2009). Lonely Planet Boston City Guide (4 ed.). Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1-74179-178-5.
Wechter, Eric B.; et al. (2009). Fodor's Boston 2009. Random House Digital, Inc. ISBN 978-1-4000-0699-1.
Further reading
Beagle, Jonathan M.; Penn, Elan (2006). Boston: A Pictorial Celebration. Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. ISBN 978-1-4027-1977-6.
Brown, Robin; The Boston Globe (2009). Boston's Secret Spaces: 50 Hidden Corners In and Around the Hub (1 ed.). Globe Pequot. ISBN 978-0-7627-5062-7.
Hantover, Jeffrey; King, Gilbert (2008). City in Time: Boston. Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. ISBN 978-1-4027-3300-0.
O'Connell, James C. (2013). The Hub's Metropolis: Greater Boston's Development from Railroad Suburbs to Smart Growth. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-01875-3.
O'Connor, Thomas H. (2000). Boston: A to Z. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-00310-1.
Price, Michael; Sammarco, Anthony Mitchell (2000). Boston's immigrants, 1840–1925. Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7524-0921-4.
Krieger, Alex; Cobb, David; Turner, Amy, eds. (2001). Mapping Boston. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-61173-2.
Seasholes, Nancy S. (2003). Gaining Ground: A History of Landmaking in Boston. Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-19494-5.
Shand-Tucci, Douglass (1999). Built in Boston: City & Suburb, 1800–2000 (2 ed.). University of Massachusetts Press. ISBN 978-1-55849-201-1.
Southworth, Michael; Southworth, Susan (2008). AIA Guide to Boston, 3rd Edition: Contemporary Landmarks, Urban Design, Parks, Historic Buildings and Neighborhoods (3 ed.). Globe Pequot. ISBN 978-0-7627-4337-7.
Vrabel, Jim; Bostonian Society (2004). When in Boston: A Time Line & Almanac. Northeastern University Press. ISBN 978-1-55553-620-6.
Whitehill, Walter Muir; Kennedy, Lawrence W. (2000). Boston: A Topographical History (3 ed.). Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-00268-5.
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Boston |
- Official website
 "Boston". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.
"Boston". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.
Historical Maps of Boston from the Norman B. Leventhal Map Center at the Boston Public Library
Boston at Curlie





